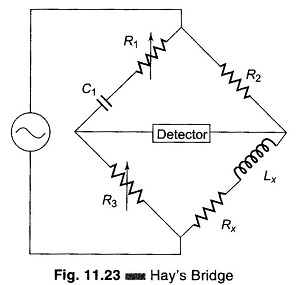
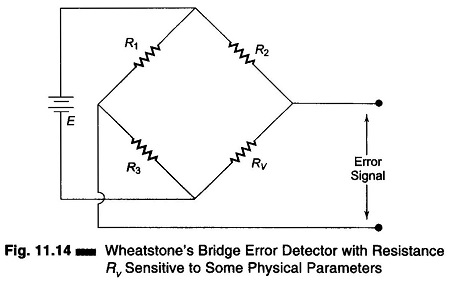
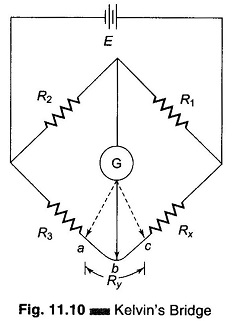
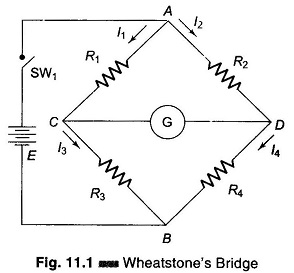
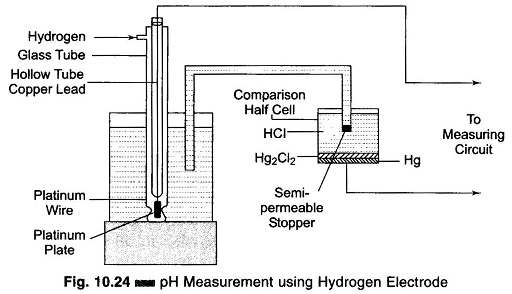
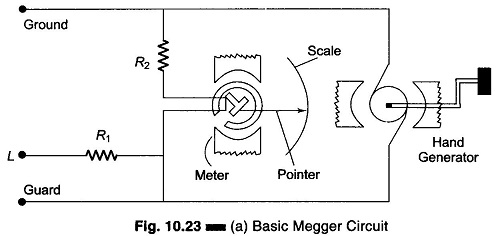
Hays Bridge Circuit
Hays Bridge Circuit: Hays Bridge Circuit, shown in Fig. 11.23, differs from Maxwell’s bridge by having a resistance R1 in series with a standard capacitor C1 instead of a parallel. For large phase angles, R1 needs to be low; therefore, this bridge is more convenient for measuring high-Q coils. For Q = 10, the error is […]
Hays Bridge Circuit Read More »