Control Systems in Electronic Instrumentation Articles:
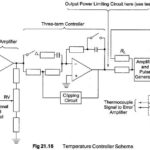
Temperature Controls using an Analog Electronic Controller: A Temperature Controls scheme using an Analog Electronic Controller of Fig. 21.14 is as shown in Fig. 21.16. The temperature setting, derived from a slide wire, is compared with the signal from a thermocouple situated in the … (Read More)
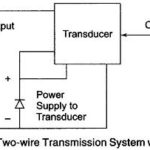
Choice of Electronic Signal Transmission: The range of air pressure used for Signal Transmission in pneumatic system is limited by the dynamic operating range of the pneumatic devices used. But the choice of electrical transmission is much wider. Since either ac … (Read More)
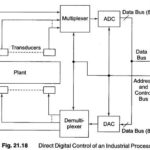
Direct Digital Control: Developments in digital electronics have led to many industrial processes being computer controlled. The first system used was Direct Digital Control (DDC), in which a computer measured each variable in the process, these signals being used to maintain … (Read More)
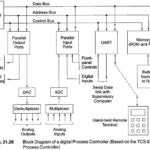
Digital Process Control: A digital process control functionally needs to operate in much the same way as a conventional analog controller. That is, it must provide facilities to raise or lower the set point and to provide proportional, 2-term or 3-term … (Read More)
Cascade Control with Digital Controllers: A simplified system to control the temperature of a process employing a gas burner using two Cascade Control digital controllers is shown in Fig. 21.21. Each controller has a number of digital inputs and outputs, and also … (Read More)
PLC Definition(Programmable Logic Controller or Programmable Controller): PLC Definition – Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or commonly simply called a Programmable Controller, is a solid state, digital, industrial computer. It is a device that was invented to replace the necessary sequential relay circuits … (Read More)
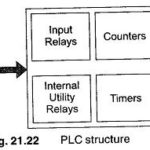
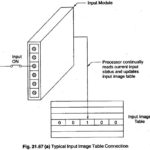
PLC Structure: The PLC Structure mainly consists of a CPU, memory areas, and appropriate circuits to receive input/output data as shown in Fig. 21.22. A PLC can be considered as a box full of hundreds of thousands of separate relays, counters, … (Read More)
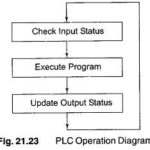
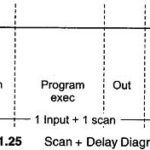
PLC System Operation: A PLC System Operation works by continually scanning a program. This scan cycle can be considered as made up of three important states as shown in Fig. 21.23. In addition there are also more than three states and … (Read More)
PLC Applications: The PLC Applications takes a certain amount of time to react to changes. The total response time of the PLC is a fact that has to be considered while selecting a PLC for some application where speed is a concern. For … (Read More)
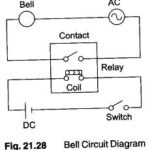
Relays Definition: The main purpose of a PLC is to replace real world relays. A Relays Definition is basically an electro-magnetic switch. When a voltage is applied to the coil, a magnetic field is generated. This magnetic field attracts the contact of … (Read More)
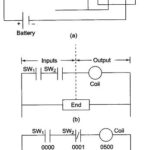
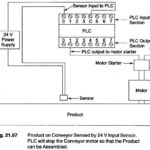
PLC Register: Let us consider a simple example and compare the ladder diagram with its real world external physically connected relay circuit. In Fig. 21.32 (a), the coil circuit will be energized when there is a closed loop between … (Read More)
Timer: Timer is an instruction that waits a set amount of time before doing something. The different kinds of timers are available with different manufacturers. Most of the timers are: ON-delay Timer: This type of timer simply “delays turning on”. In other … (Read More)
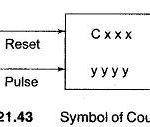
Symbol Counter: A counter is a simple device used for counting. There are different types of counters. There are up-counters (that only count up 1, 2, 3 …). These are called CTU (Count up), ‘CM’, C or CTR. There are … (Read More)
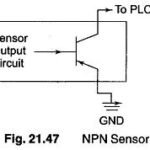
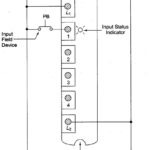
DC Inputs: The, dc inputs modules commonly available will work with 5, 12, 24 and 48 volts. The DC Inputs modules allow us to connect either PNP (sourcing) or NPN (sinking) transistor type devices to them. If using a regular switch (i.e. … (Read More)
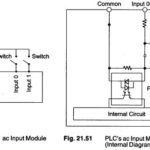
AC Input: The, ac input modules that are commonly available work with 24, 48, 110 and 220 V. It is important to use the one that fits the needs based upon the inputs devices (voltage) used. These day, ac input modules are … (Read More)
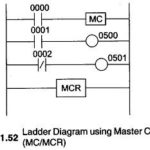
Master Control: Master control can be considered the emergency stop switches. An emergency stop switch typically is a big red button on a machine that will shut it off in cases of emergency. It is commonly abbreviated as MC/MCR (Master control … (Read More)
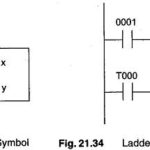
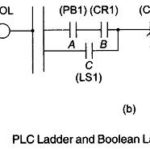
PLC Programming Languages: The term PLC programming languages refers to the method by which the user communicates information to the PLC. The two most common language structures are ladder diagram language and Boolean language. Ladder diagram language is by far the most … (Read More)
PLC Basic Process: A PLC Basic Process is basically made up of the following sections, each of which has a unique function to perform in its operation. The sections are: Sensing inputs or controlling hardware PLC input hardware Controller or CPU Hand held programming device … (Read More)
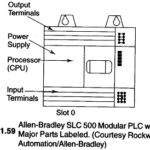
PLC Hardware: PLC hardware falls into the following physical configuration: Fixed Input/ Output (I/O) and Modular I/O. 1.Fixed 1/0 PLCs A fixed PLC Hardware consists of a fixed, or built-in, input/output section. There is one fixed or built-in, non removable screw terminal strip containing all … (Read More)
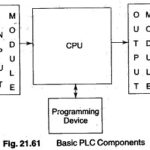
PLC Components: A PLC is a solid state device designed to perform logic functions previously accomplished by electro-magnetic relays. Basically, the PLC Components is an assembly of solid state digital logic decisions which provides outputs. PLCs are used for the control … (Read More)
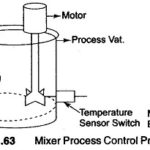
PLC Operation: To understand the PLC Operation, consider the simple process shown in Fig. 21.63 In this process a mixer motor is to be used to automatically stir the liquid in a vat when the temperature and pressure reach a preset … (Read More)
Basis of PLC Programming: 1.Processor Memory Organisation: The term processor memory organization refers to how certain areas of memory in a given Basis of PLC Programming are used. Different PLC manufacturers organize their memories in different ways. Even though they do not … (Read More)
PLC Hardware Components: 1. PLC Hardware Components – The input and output interface modules consists of an I/0 rack and individual I/O modules. Input interface modules, accept signals from the machine or process devices (120V ac) and convert them into signals … (Read More)
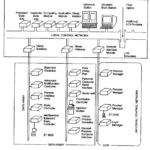
Distributed Control System: Since the beginning of process control in late 1970s, it has made great progress in every control activity. Similar to the other electronic equipment, its size is decreasing and its power is increasing. The … (Read More)
DCS System: A DCS System is preferred over a central computer system for the following reasons. Central Computer System (CCS) exposes the plant to the risk that the system might fail. This can be minimized by having one or more back up … (Read More)
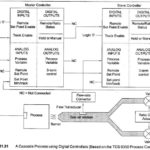
TDC 3000 Architecture: 1. Hiway Based Distributed Control: The building block concept of TDC 3000 Architecture control design, with distributed process controlled boxes linked together by a communication network, was first introduced by Honeywell in 1975. Today, the monitor and control boxes … (Read More)
Microprocessor Based DCS: Modern plants nowadays are very complex, large scale systems with a very high degree of automation. The designs and the operation of these plants are determined by the criteria of economy availability and safety. … (Read More)