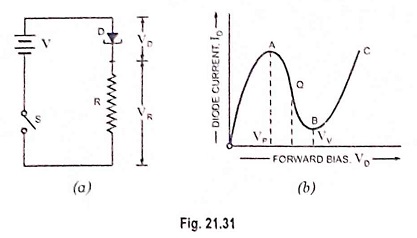
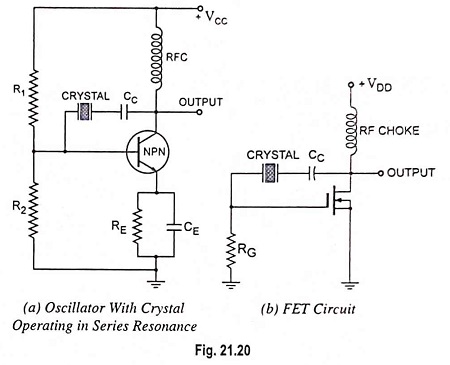
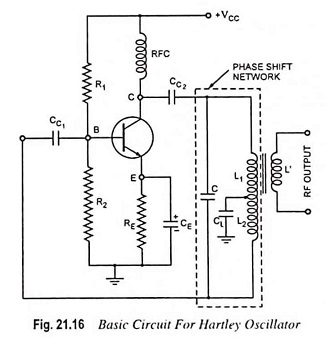
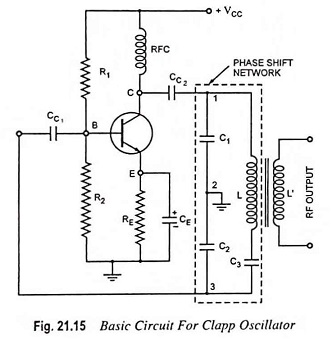
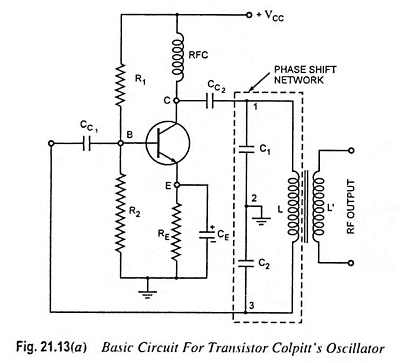
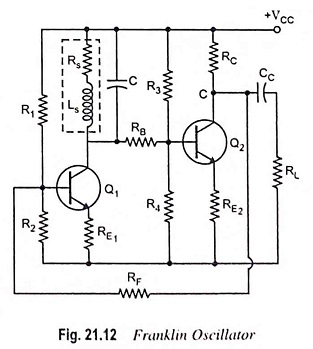
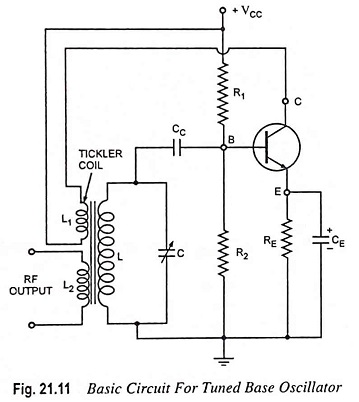
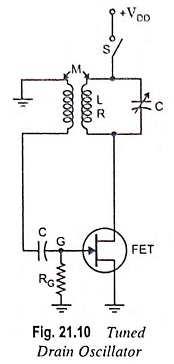
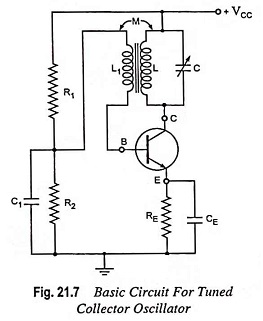
Selection of Oscillator
Selection of Oscillator: While in the Selection of Oscillator for a particular application, the following particulars are to be considered. Frequency Range: The oscillator selected for a particular application should be capable of supplying an…