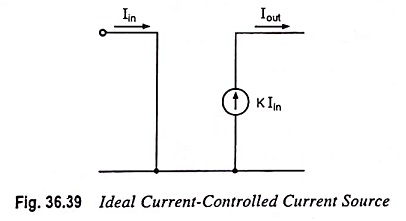
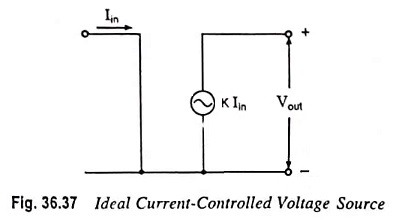
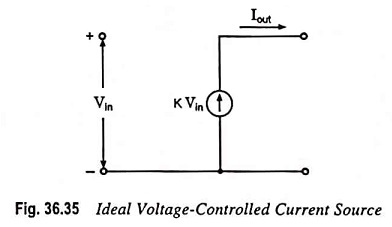
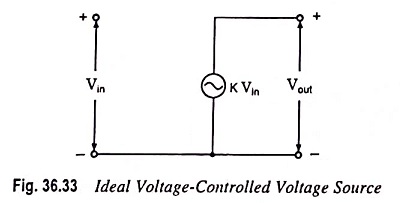
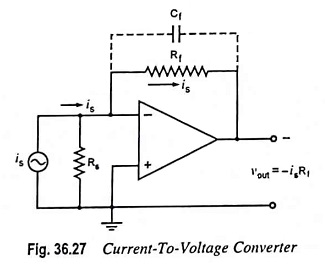
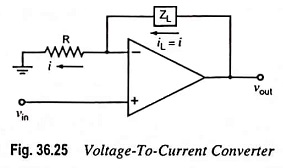
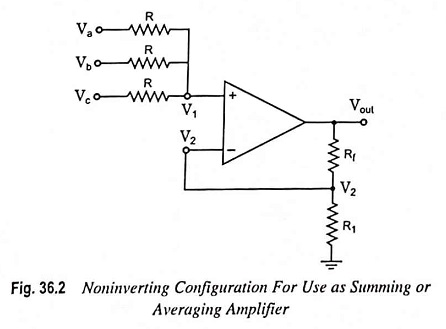
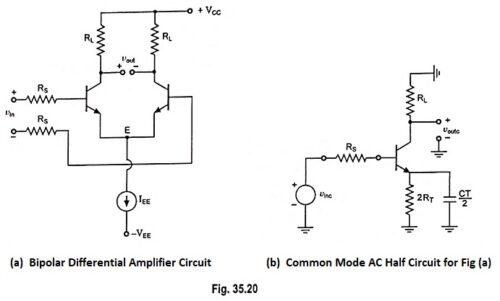
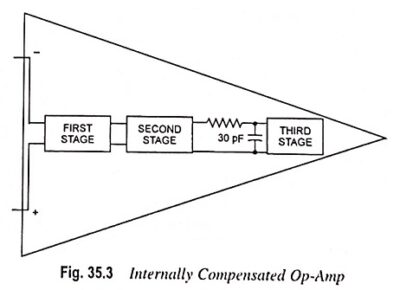
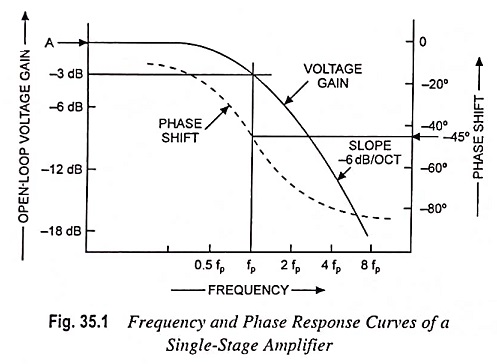
Current Controlled Current Source (CCCS) Circuit
Current Controlled Current Source (CCCS) Circuit: An ideal form of a Current Controlled Current Source (CCCS) Circuit by an input current is shown in Fig. 36.39. Such a circuit provides an output current dependent on…