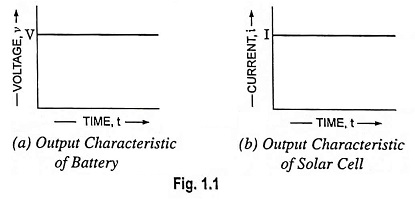
Zero Reference Level in Electronics Engineering
Zero Reference Level in Electronics Engineering: Zero Reference Level - In order to avoid errors in the measurement of different voltages in an electronic circuit, it is imperative to select some common point, known as…