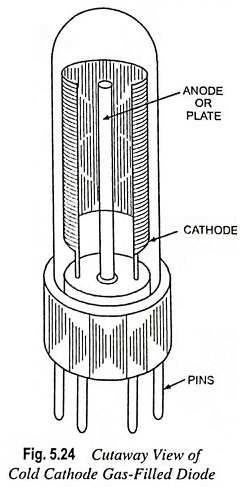
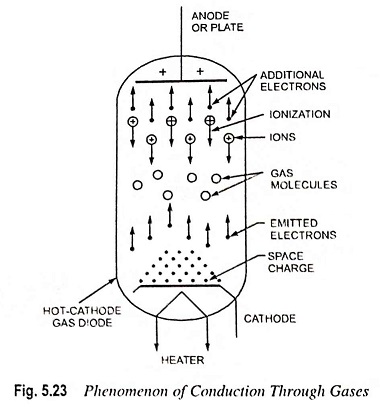
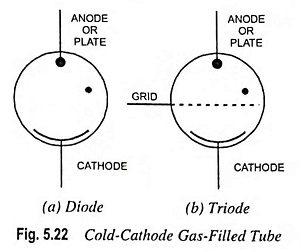
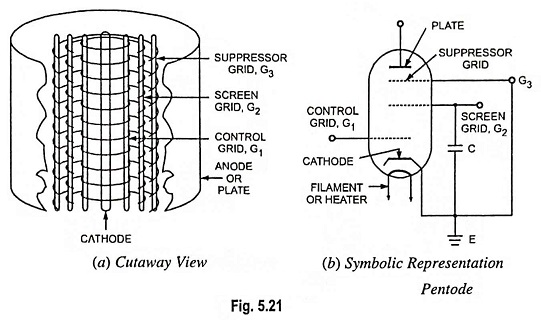
Energy Band Theory of Crystals
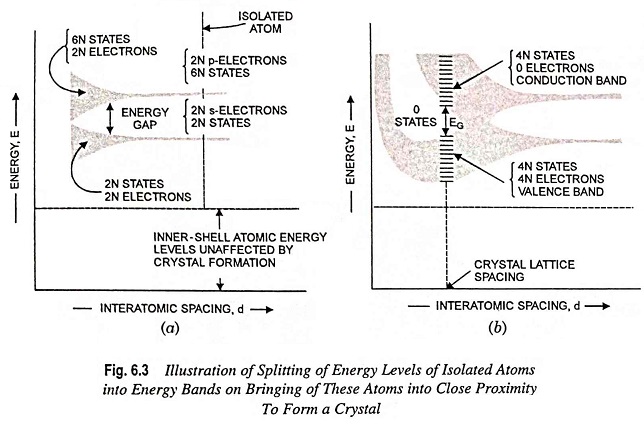
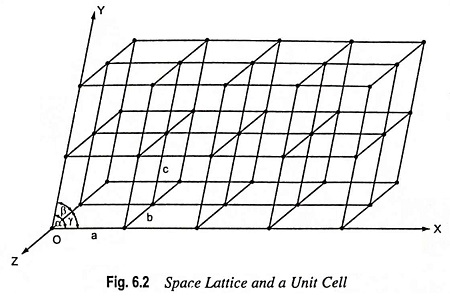
Energy Band Theory of Crystals: Energy Band Theory of Crystals – As discussed above, it is revealed that most metals and semiconductors are crystalline in structure and a crystal is made up of a space array of atoms or molecules (strictly speaking, ions) in regular repetition in three dimensions of some fundamental structural unit. For […]
Energy Band Theory of Crystals Read More »