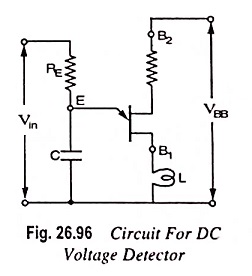
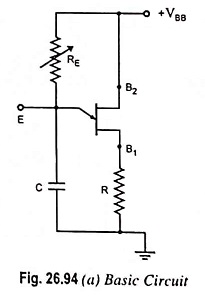
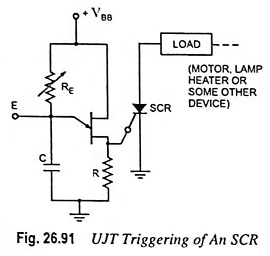
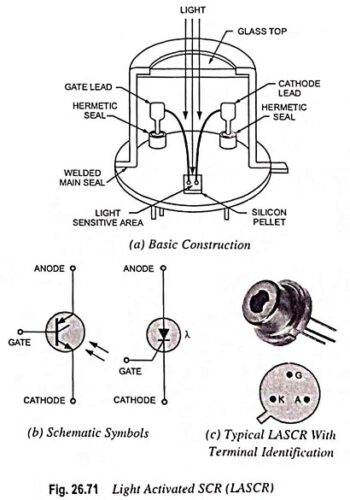
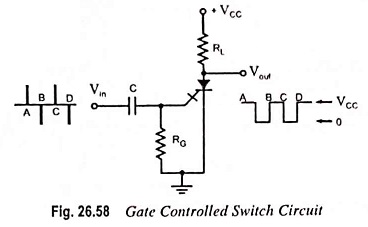
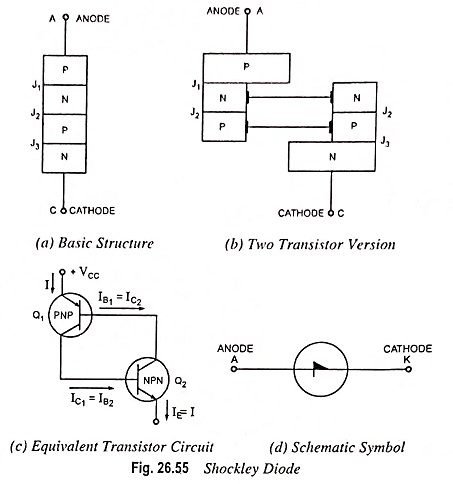
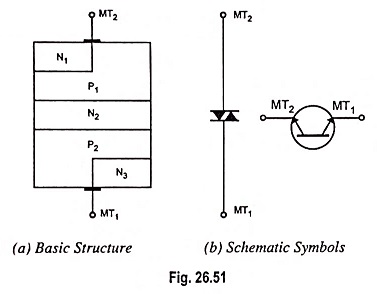
UJT as Over Voltage Detector Circuit Diagram
UJT as Over Voltage Detector Circuit Diagram: UJT as Over Voltage Detector Circuit Diagram - A simple dc overvoltage detector circuit is given in Fig. 26.96. It operates on the fact that the device remains…