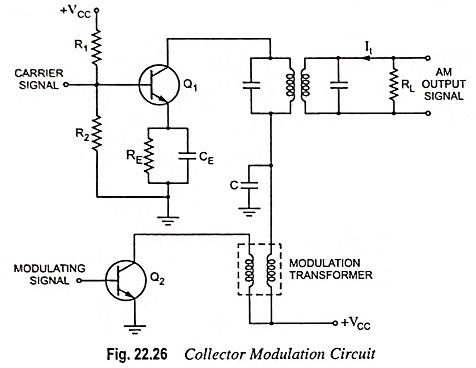
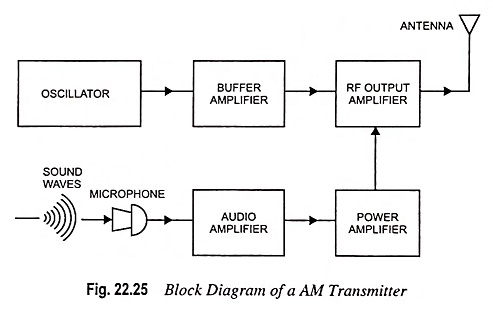
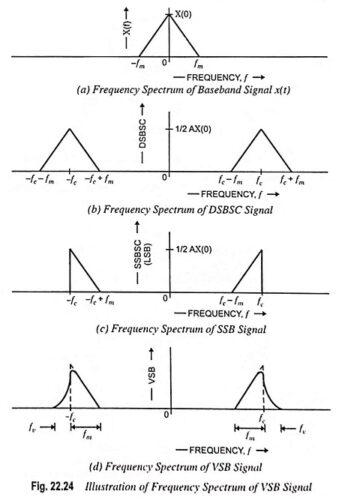
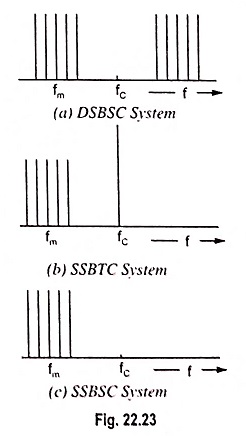
Generation of DSBSC Signal using Balanced and Ring Modulator
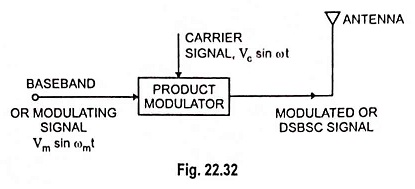
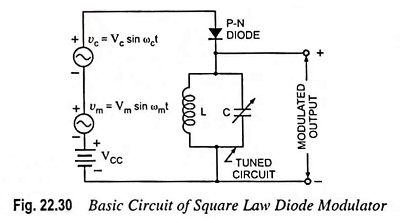
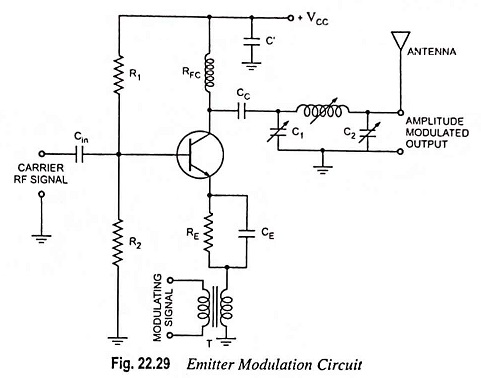
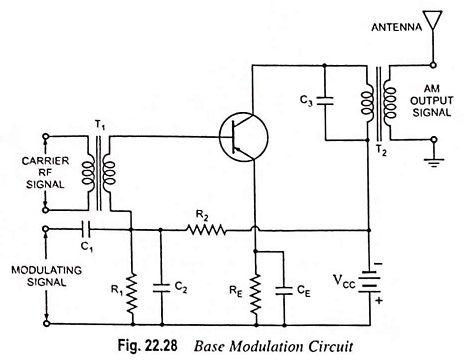
Generation of DSBSC Signal using Balanced and Ring Modulator: DSBSC signal can be obtained by simply multiplying the modulating signal with the carrier signal. By simple multiplication of Vc sin ωct and Vm sin ωmt, we have the…