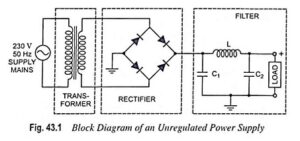
What is Clipper Circuit? – Definition and Classification
Clipper Circuit is one which controls the shape of the waveform by removing or “clipping” off an unwanted portion. A half-wave rectifier is an example of the simplest form of clipper as it passes only the positive (or negative) half cycle of an alternating waveform and clips off the other half cycle. Clipper Circuit find extensive use in radars, digital computers and other electronic systems for removing unwanted portions of the input signal voltages above or below a specified level. Another application is in radio receivers for communication circuits where noise pulses, that rise well above the signal amplitude, are clipped down to the desired level. Clipper Circuit are also referred to as voltage limiters, amplitude selectors or slicers.
Clipping circuit consists of nonlinear and linear devices. The nonlinear devices generally used for clipping are diodes and transistors. According to nonlinear devices used, clippers may be classified as diode clippers and transistor clippers.
According to biasing, the clippers may be classified as
- unbiased clippers and
- biased clippers.
According to configuration used the clippers may be
- series diode clippers
- parallel or shunt diode clippers
- a series combination of diode, resistor and reference supply
- Multidiode clippers consisting of several diodes, resistors and reference voltages
- two emitter-coupled transistors operating as an overdriven difference amplifier.
According to level of clipping the clippers may be
- Positive clippers
- Negative clippers
- Biased clippers and
- Combination clippers.