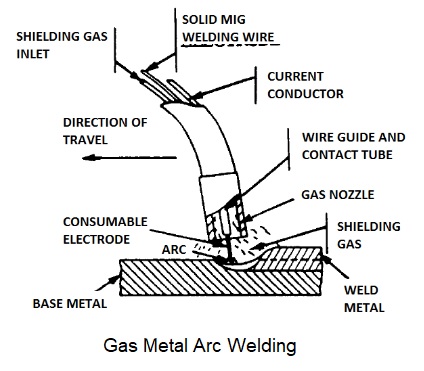
Gas Metal Arc Welding – Working Principle, Advantages and Applications:
It is a gas shielded, gas metal arc welding process which uses the intense heat of an electric arc between a continuously fed, consumable electrode wire and the material to be welded. A consumable bare electrode wire producing the filler metal is automatically fed from a reel on to the job through a welding gun which also carries a nozzle. Through this nozzle helium or argon is blown around the arc and on to the weld. Because of low arc voltage for a given welding current argon is suitable for thin materials as tendency to burn through is reduced. Because of low arc voltage and low power for given welding current in case of argon gas welding tendency for metal fusion and metal sag or run is reduced and, therefore, it is preferred for inposition welding.
On the other hand, because of high arc voltage and high power in case of helium gas welding, it is used for welding of thick materials and metals with high heat conductivity. Mixture of the two gases is useful to get intermediate characteristics. AC and dc both can be used.
Advantages:
- In this method concentration of heat is possible and thus distortion is minimized.
- In this method no flux is required since atmosphere is inert and air does not come in contact with the molten metal.
Applications:
This Gas Metal Arc Welding process is particularly employed for welding light alloys, stainless steel and non-ferrous metals such as copper, aluminium and their alloys. For welding aluminium and aluminium alloys ac supply and argon gas is used where as for welding magnesium and magnesium alloys either ac supply and argon gas or dc supply, reversed polarity and either argon or helium gas is used. For the welding of stainless steel, mild steel, copper and copper alloys, dc and either argon or helium or ac high frequency stabilized with argon or helium used.