Three phase Transformer Bank of Single phase Transformers
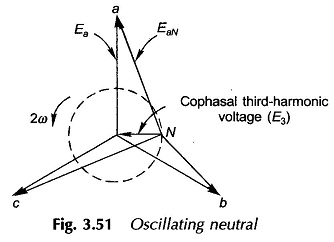
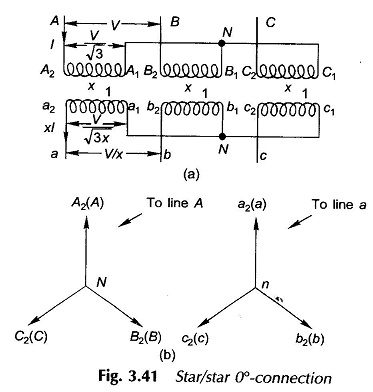
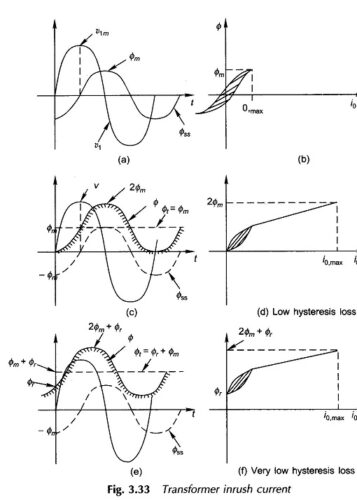
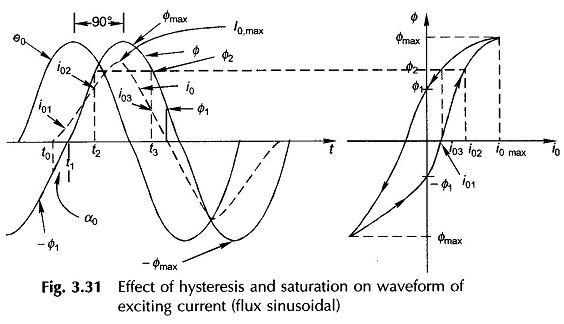
Three phase Transformer Bank of Single phase Transformers: The different Three phase Transformer Bank of Single phase Transformers are namely, Delta/delta connection: The supply voltage provides only sinusoidal magnetizing current so that core flux is flat-topped; but the third-harmonic emfs induced (cophasal) cause circulating currents in deltas restoring the flux to almost sinusoidal. The third-harmonic […]
Three phase Transformer Bank of Single phase Transformers Read More »