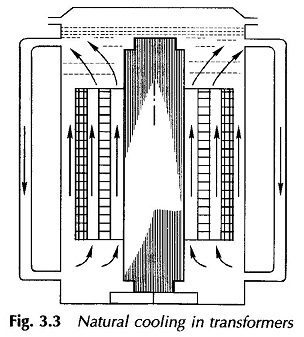
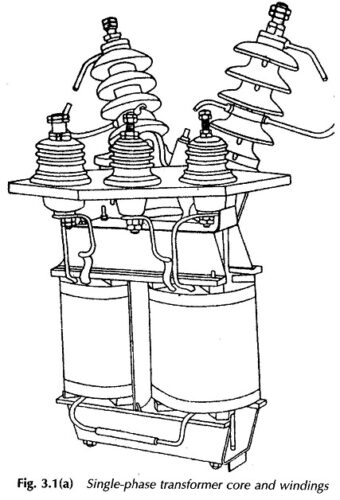
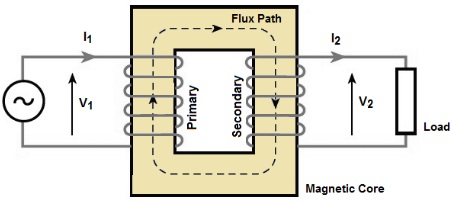
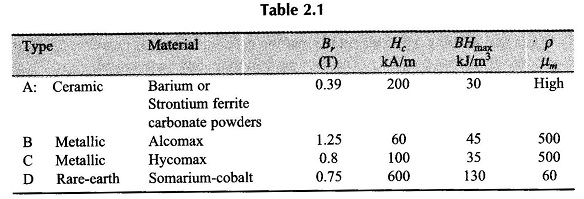
Natural Cooling System in Transformer
Natural Cooling System in Transformer: Natural Cooling System in Transformer – Smaller size transformers are immersed in a tank containing transformer oil. The oil surrounding the core and windings gets heated, expands and moves upwards. It then flows downwards by the inside of tank walls which cause it to cool and oil goes down to […]
Natural Cooling System in Transformer Read More »