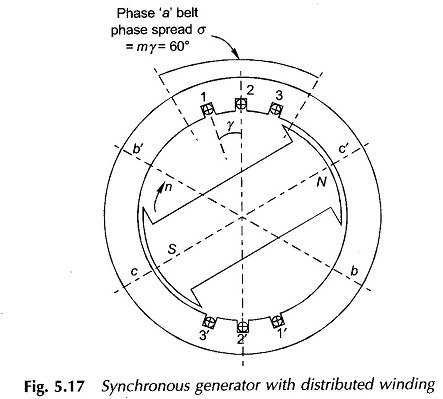
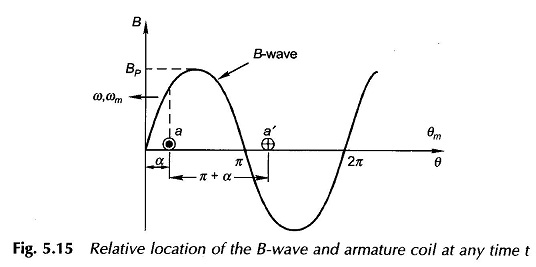
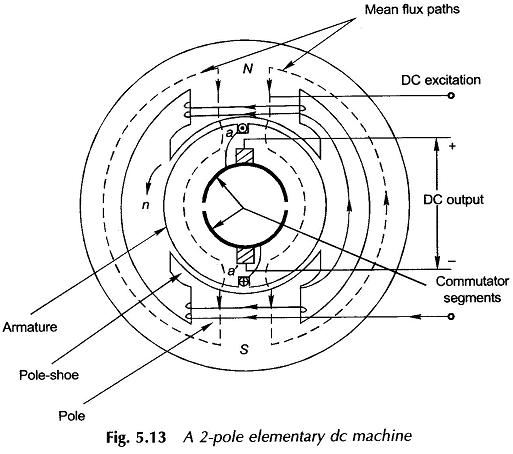
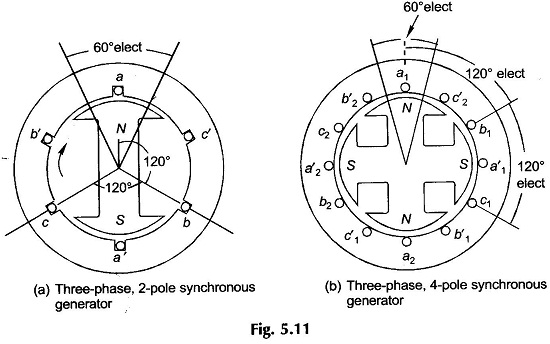
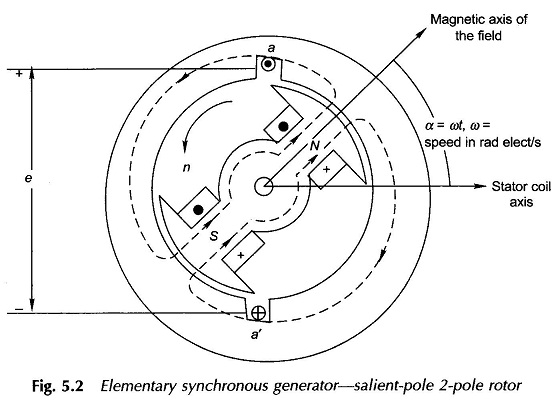
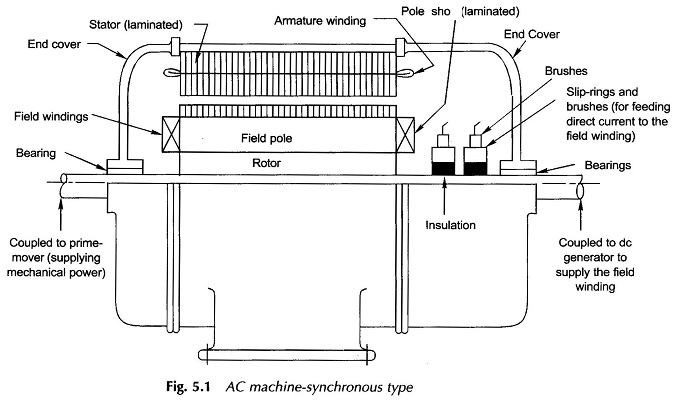
Synchronous Generator with Distributed Winding
Synchronous Generator with Distributed Winding: Synchronous Generator with Distributed Winding – It may be seen from Eq. (5.7) that the flux/pole is limited by the machine dimensions and the peak flux density which cannot exceed a specified value dictated by saturation characteristic of iron. Therefore, for inducing an emf of an appropriate value in a […]
Synchronous Generator with Distributed Winding Read More »