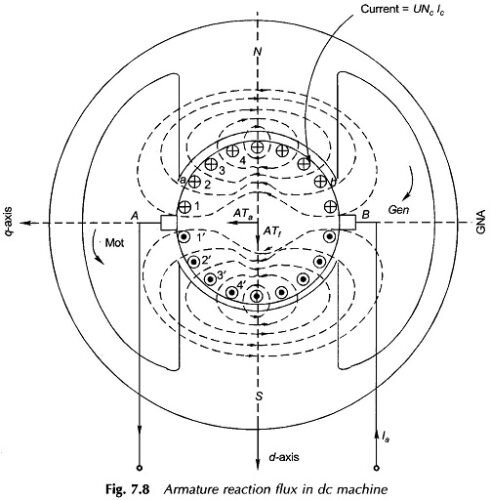
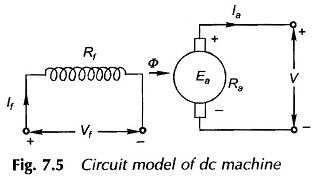
External Characteristics of Compound Generator
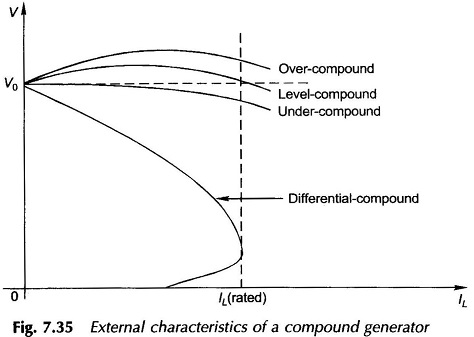
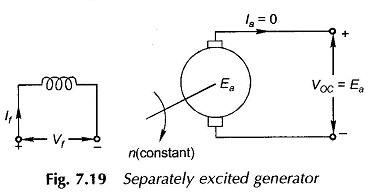
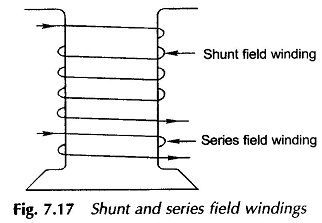
External Characteristics of Compound Generator: External Characteristics of Compound Generator – The causes of voltage drop in the terminal voltage from no-load to full-load in a shunt generator can be partially/fully/over-compensated by use of an aiding series field (cumulative compound), which can be connected in a long- or short-shunt (long-shunt shown in. Fig. 7.34). The […]
External Characteristics of Compound Generator Read More »