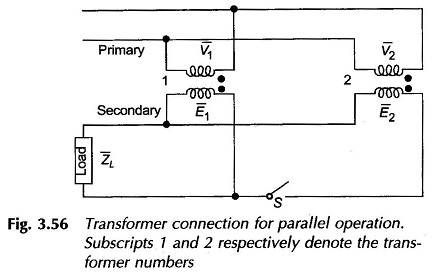
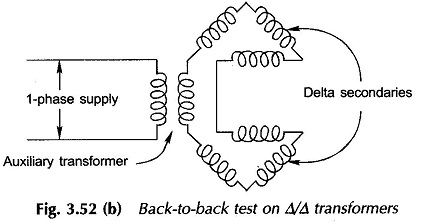
Principle of Electromechanical Energy Conversion
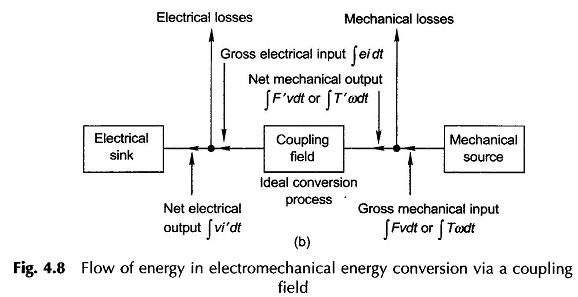
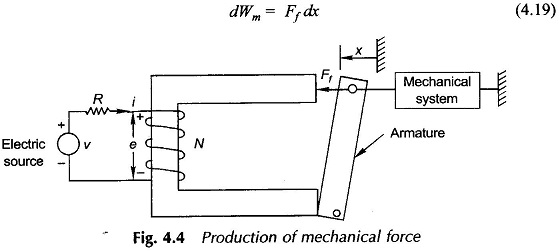
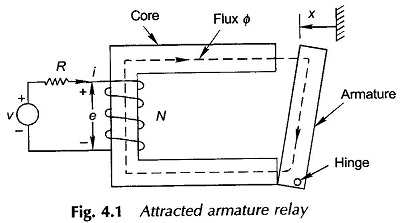
Principle of Electromechanical Energy Conversion: Principle of Electromechanical Energy Conversion is a reversible process and Eqs (4.26) to (4.29) govern the production of mechanical force. In Fig. 4.4 if the armature is allowed to move on positive x direction under the influence of Ff, electrical energy is converted to mechanical form via the coupling field. If […]
Principle of Electromechanical Energy Conversion Read More »