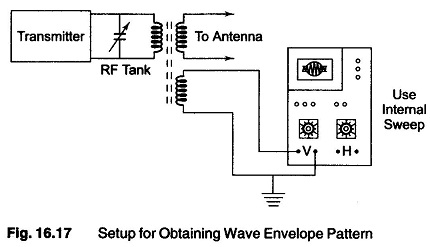
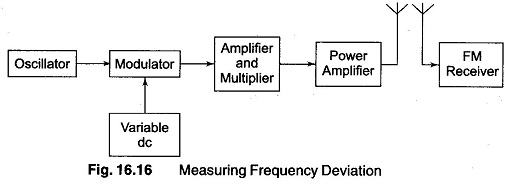
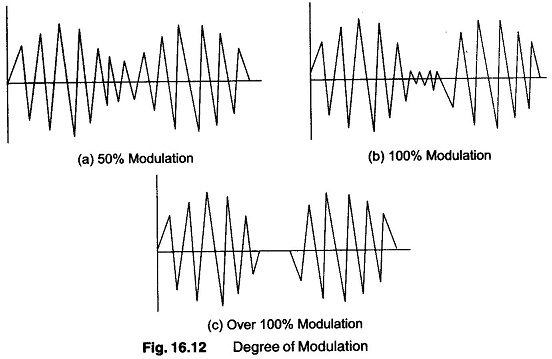
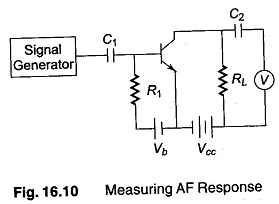
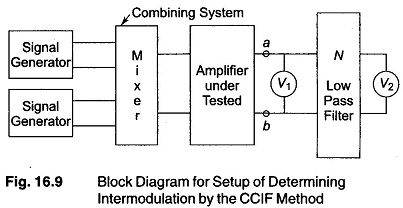
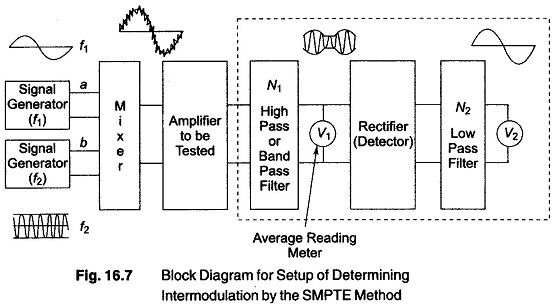
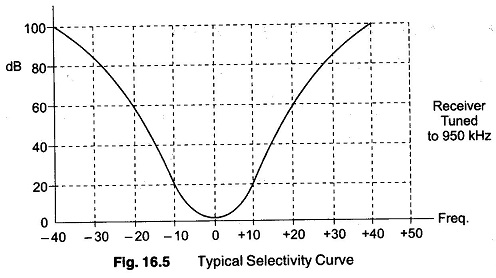
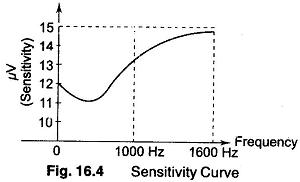
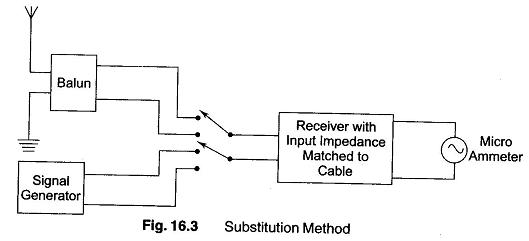
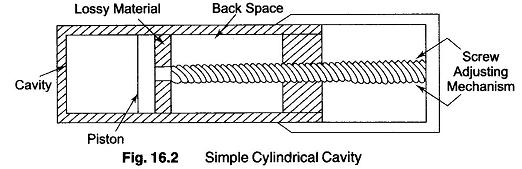
Measuring Amplitude Modulation
Measuring Amplitude Modulation Using CRO: The CRO is widely used as an Measuring Amplitude Modulation. It presents the waveform for visual monitoring and is fairly accurate in measurements of modulation percentage. The type of CRO…