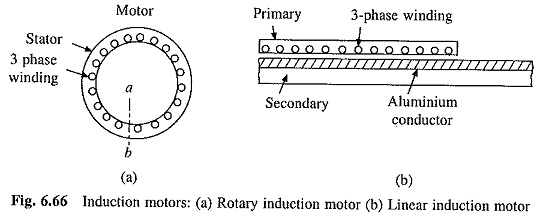
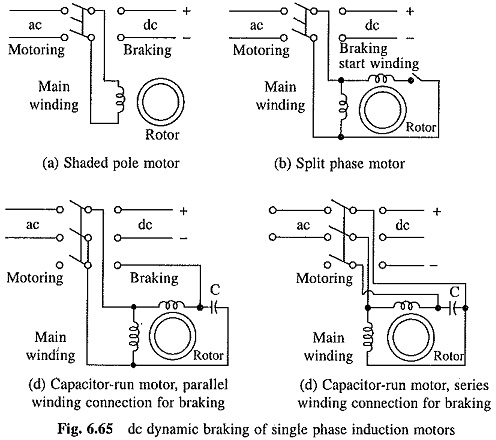
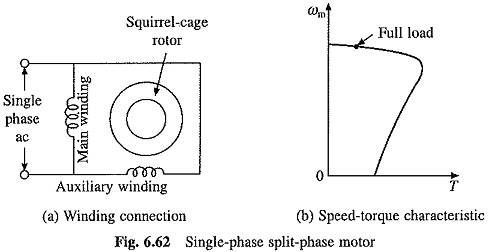
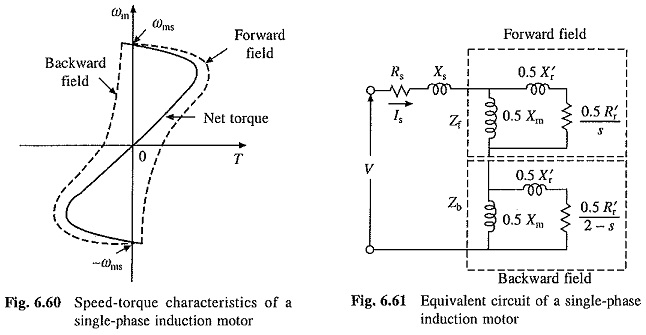
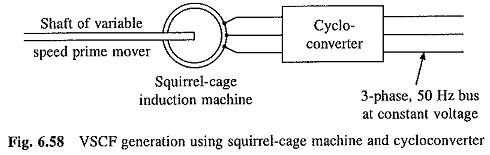
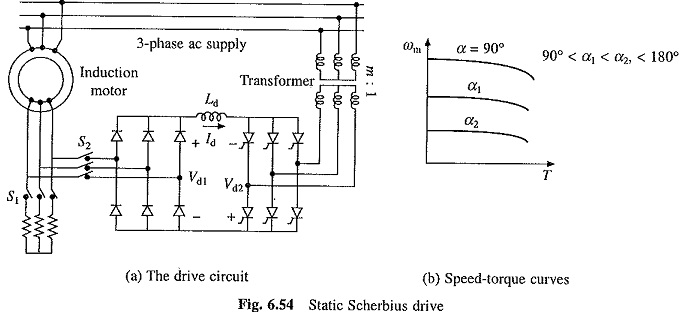
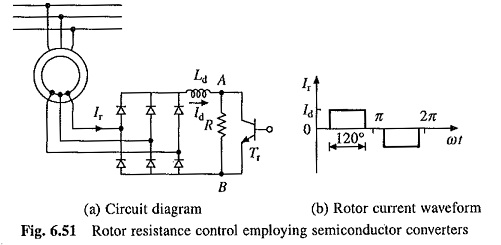
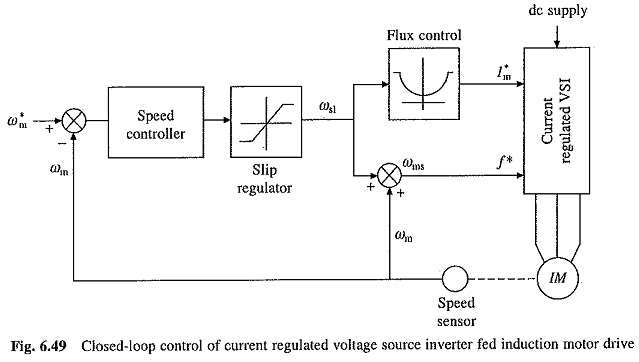
Working Principle of Linear Induction Motor
Working Principle of Linear Induction Motor: While the conventional induction motor gives rotary motion, a Working Principle of Linear Induction Motor provides translational or linear motion. Hence it is termed linear induction motor. To understand…