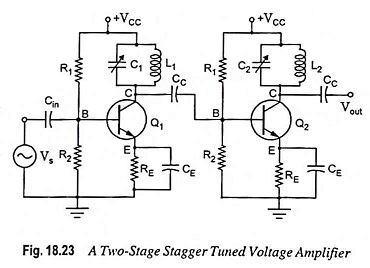
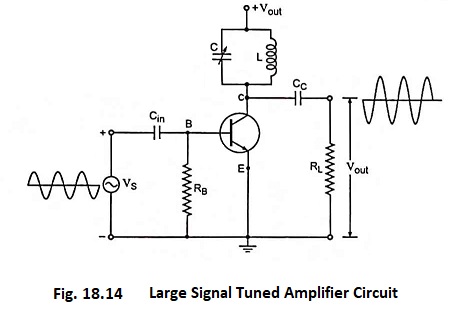
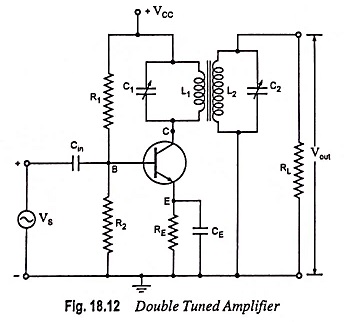
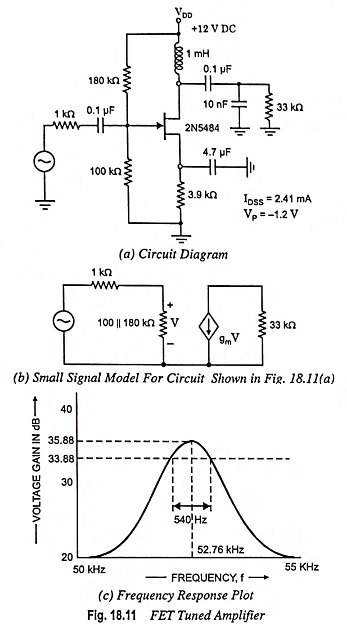
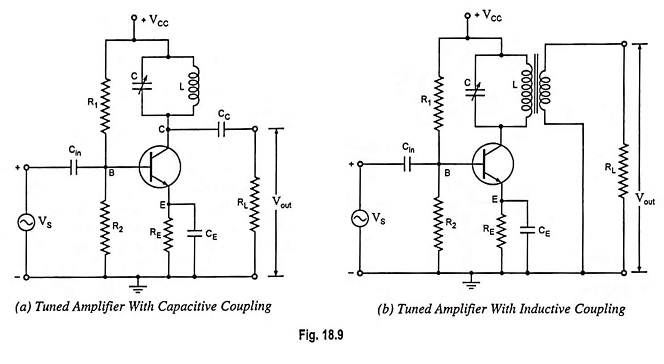
Stagger Tuned Amplifier – Circuit diagram and its Workings
Stagger Tuned Amplifier - Circuit diagram and its Workings: In order to increase bandwidth, double tuned amplifiers are preferred, but their alignment is difficult. A much better overall response can be had by stagger tuning,…