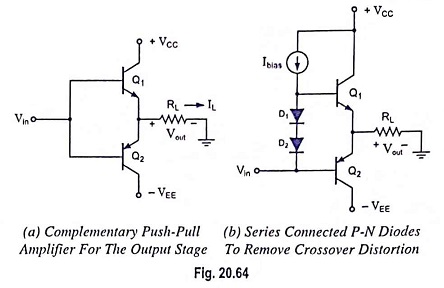
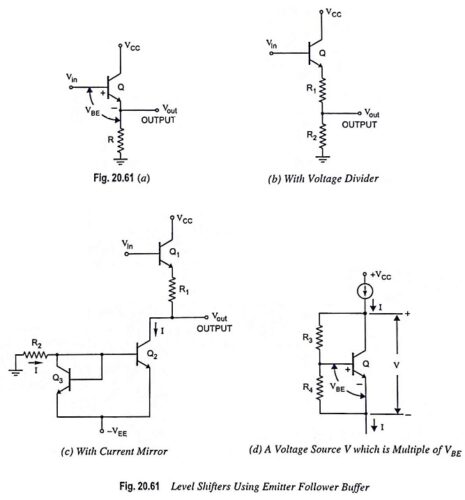
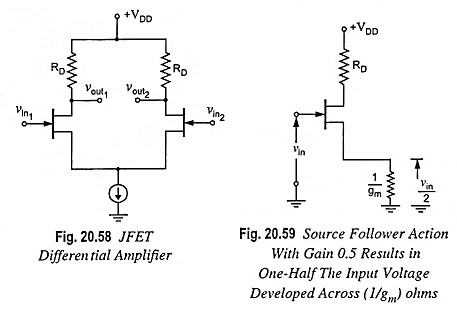
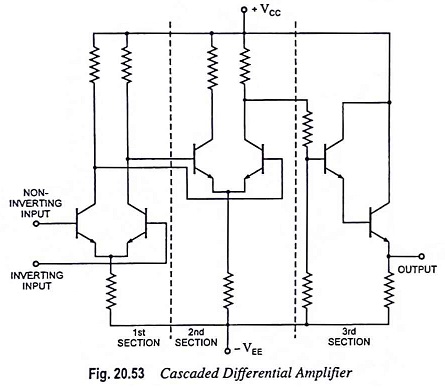
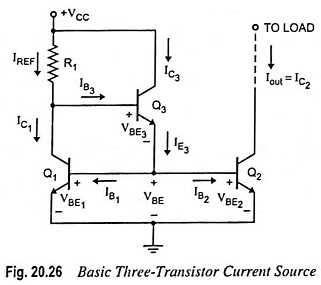
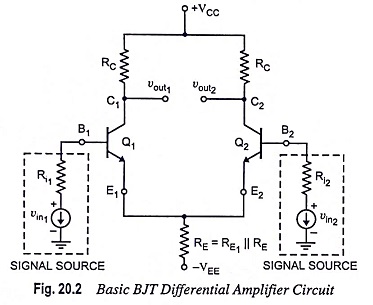
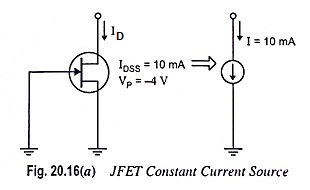
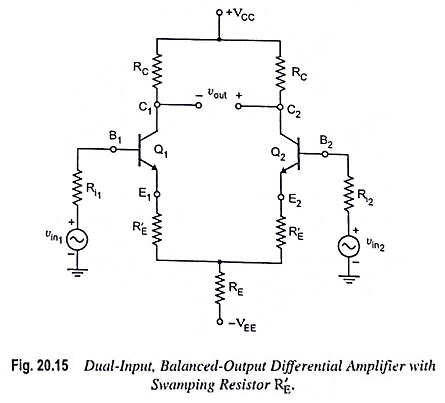
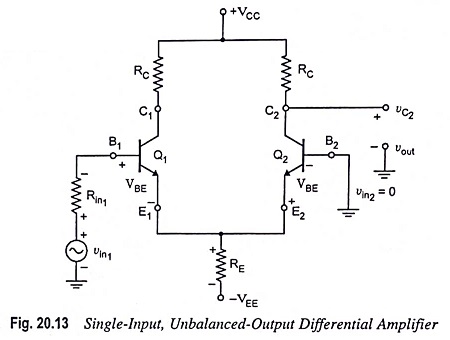
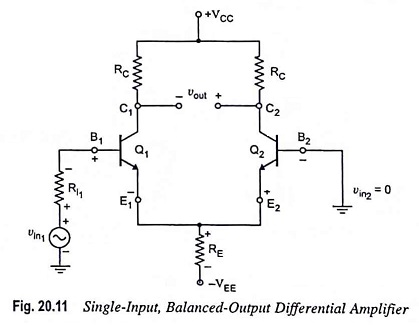
Output Stage of an Op Amp and its Voltage Transfer Characteristics
Output Stage of an Op Amp and its Voltage Transfer Characteristics: The output stage of an op amp is another requirement which should have very small output impedance and provide the external load current so…