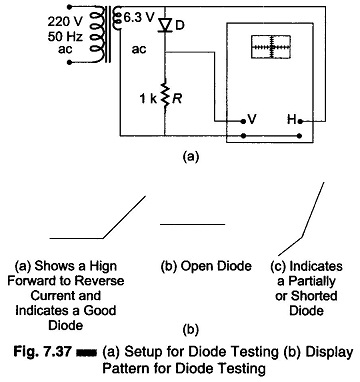
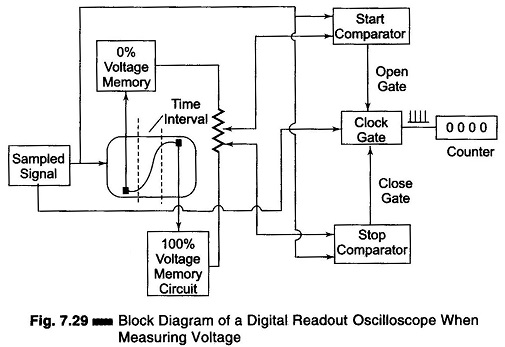
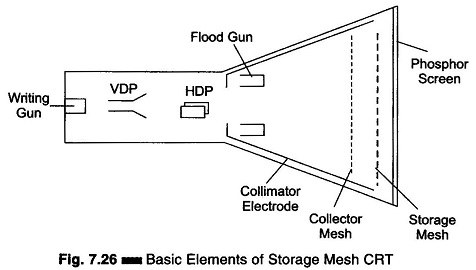
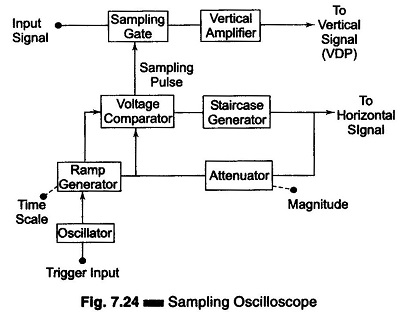
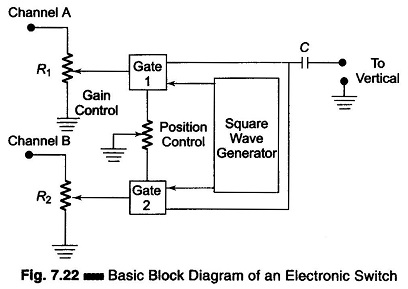
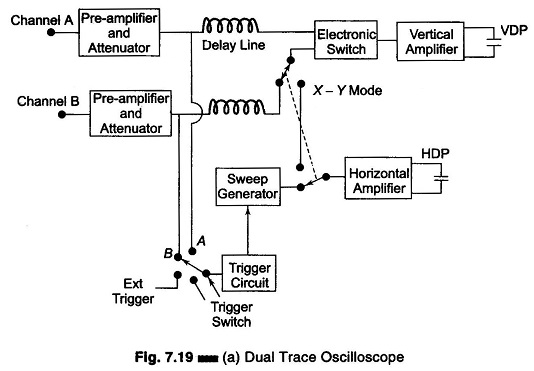
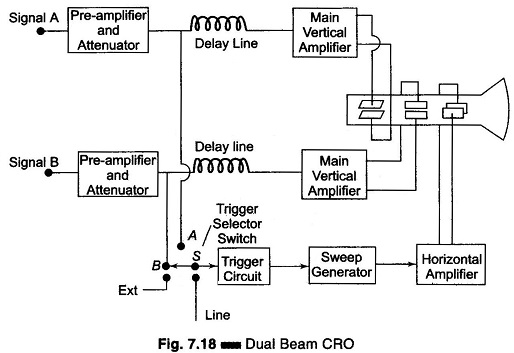
Setup for Diode Testing in Oscilloscope
Setup for Diode Testing in Oscilloscope: Diode Testing in Oscilloscope -The voltage-current characteristics curve of a crystal diode may be observed using the circuit given in Fig. 7.37 (a). In this case the internal sweep…