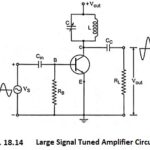
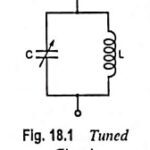
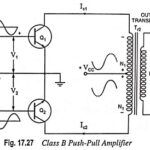
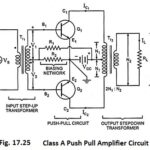
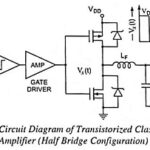
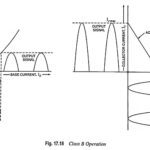
Large Signal Tuned Amplifier – Operation and its Equivalent Circuit
Large Signal Tuned Amplifier - Operation and its Equivalent Circuit: Tuned amplifier circuits are for class A operation and their use is limited to applications in which RF signal has…