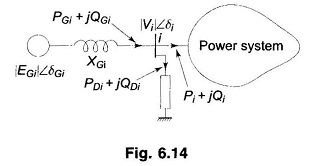
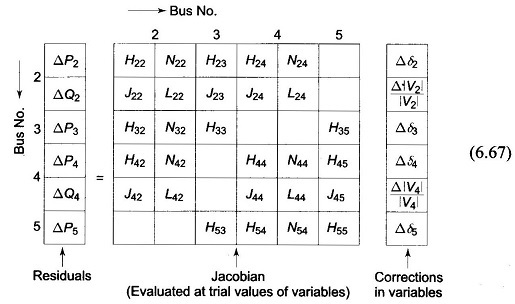
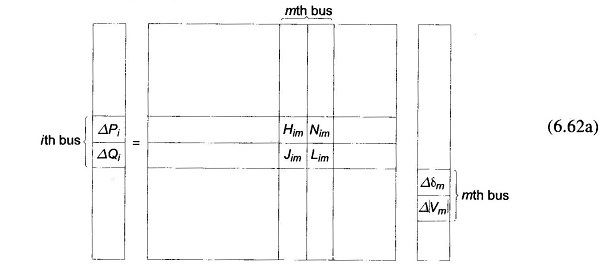
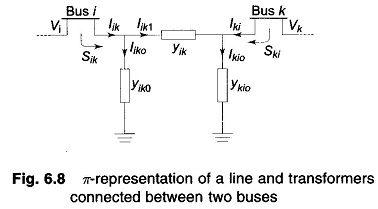
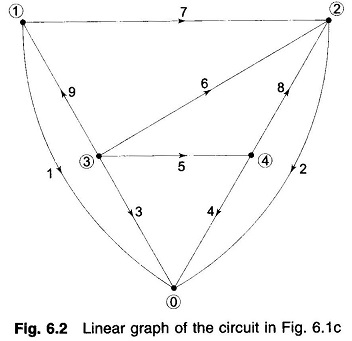
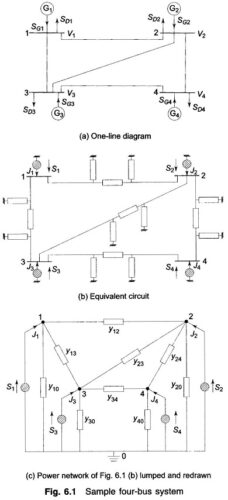
Voltage Profile of Transmission Line
Voltage Profile of Transmission Line: Control of Voltage Profile of Transmission Line at the receiving bus in the fundamental two-bus system was discussed already. Though the same general conclusions hold for an interconnected system, it…