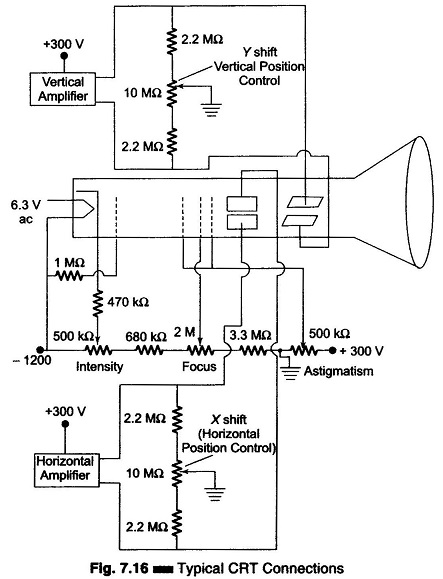
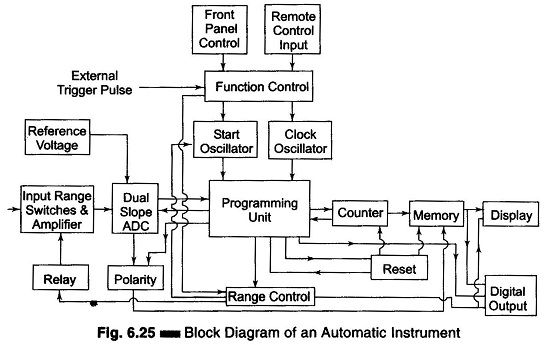
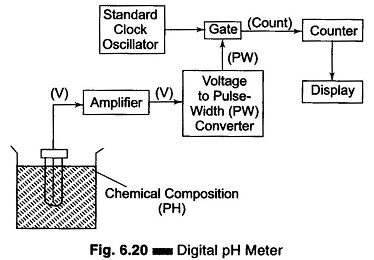
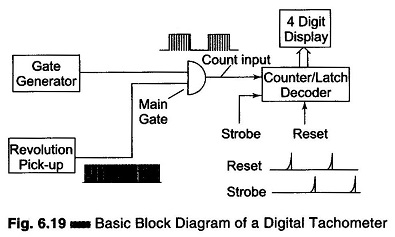
Microprocessor Controlled Bridge
Microprocessor Controlled Bridge: Microprocessor Controlled Bridge - Digital computers have been used in conjunction with test systems, bridges, and process controllers for several years. In these applications, computers were used to give instructions and perform…