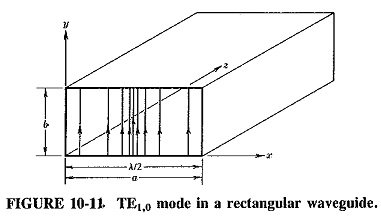
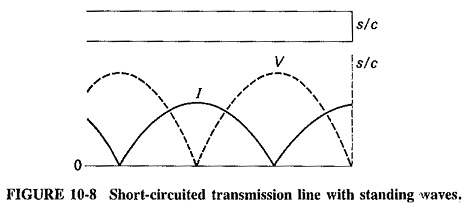
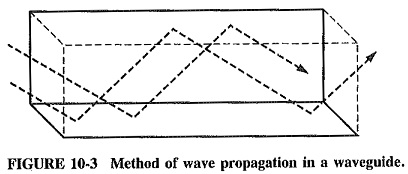
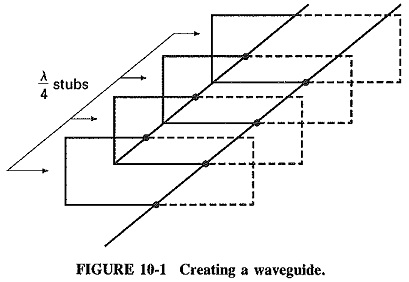
Rectangular Waveguide Derivation
Rectangular Waveguide Derivation: When the top and bottom walls are added to our parallel-plane waveguide, the result is the standard Rectangular Waveguide Derivation used in practice. The two new walls do not really affect any…