Water Cooler Working Principle and Types:
Water is one of the most needed thing for a person. In summer season cold water gives life to a thirsty person. At 10°C water is most refreshing. Thus cooling of water in summer season becomes necessary. Water coolers are used to produce cold water at about 7 to 13°C. The temperature of water is controlled with the help of a thermostatic switch.
Water coolers may be classified as follows:
- Bottle type water cooler,
- Pressure type water cooler,
- Self-contained or remote type water cooler.
Instantaneous Type Water Coolers:
In this type of coolers the cooling coil is wrapped round the pipeline such that by the time water reaches the tank it is cooled to desired temperature. Various types of instantaneous type water coolers are described below.
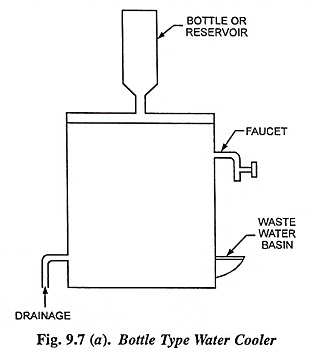
1. Bottle Type Water Cooler: In this type of water cooler, water to be cooled is stored in a bottle or reservoir. For filling glass tumblers or containers faucet or similar means are provided. The dripping water from the faucet is collected in the waste water basin or water drip, as illustrated in Fig. 9.7 (a). The usual size is 25 litres and is suitable for places where plumbing installation is expensive and drains are available.
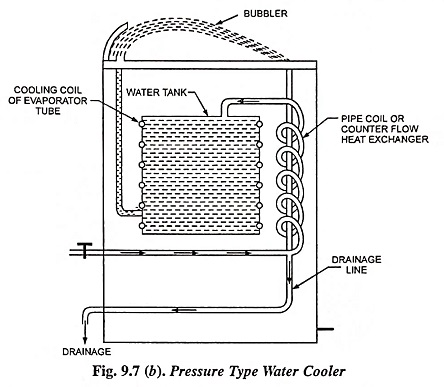
2. Pressure Type Water Cooler: In this type of cooler shown in Fig. 9.7 (b), water is supplied under pressure. For filling glass tumblers or containers faucets or similar means are provided. A valve is employed to control an appropriate flow of water or projected stream of water from a bubbler. An arrangement should be made to collect water and allow complete collection of water spreading from the bubbler. The temperature of waste water is low, it is used for cooling the supply water by passing through a pipe coil wrapped round the drainage line. By doing so, the cooling load for cooler is reduced. Since the water is supplied under pressure the cold water can be obtained from the top mounted at any height of the cooler. In case of bottle type, faucet has to be at a height up to which syphoned water can be obtained from the tank of the cooler. The refrigeration system is usually mounted at the bottom structure of the cooler body and a cooling coil is wrapped round the water tank. To ensure good surface contact between the evaporative tube and tank, either the tank surface is corrugated to accommodate pipe or pipes are secured using soft solder to provide metal contact. Sometimes a helical or U-type coil is immersed in the water tank. Although such as arrangement provides high heat transfer from water to the coil but formation of undesirable salt due to chemical reaction between water contaminant and the copper surface proves to be a great drawback in this system.
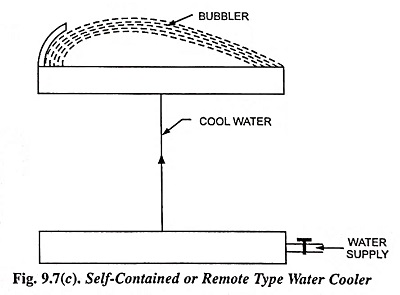
3. Self-Contained or Remote Type Water Cooler: This type of cooler [Fig. 9.7 (c)] employs mechanical refrigeration system and is a factory assembled unit. A remote type water cooler cools the water which is supplied to the desired drinking place (away from the system). It is quite a useful unit as it does not need extra space near the place of work.
Storage Type Water Cooler:
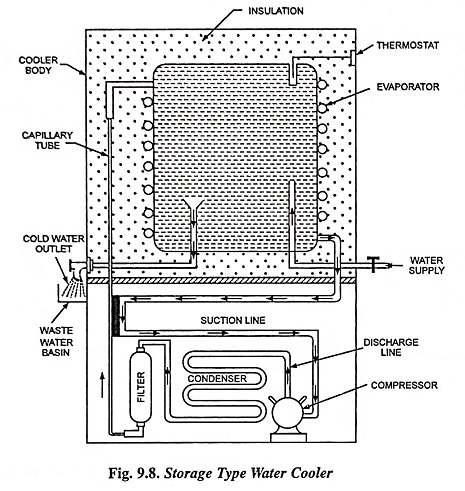
Such type of water coolers are used where continuous supply of water is not available. Fig. 9.8 shows a schematic storage type water cooler which is a self-explanatory. Here water is filled in the storage tank and level of water is kept the same by the use of a float valve. The storage tank is surrounded by an evaporator coil through which flows a low pressure liquid refrigerant which takes away the heat of water and thus makes it cold. When the water attains the desired temperature the thermostat operates and disconnects the power supply to the motor. The motor employed is capacitor-start capacitor-run single phase induction motor.
Capacity of Water Coolers:
For determination of cooling load for the water cooler (Q) the following relation may be used
Q = mw x Cp (Ti – T0)
where mw is rate of water consumption in kg, Cp is the specific heat of water in kJ/kg/K, Ti is the temperature of inlet water and T0 is the temperature of outlet water.