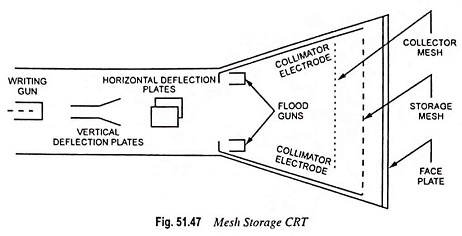
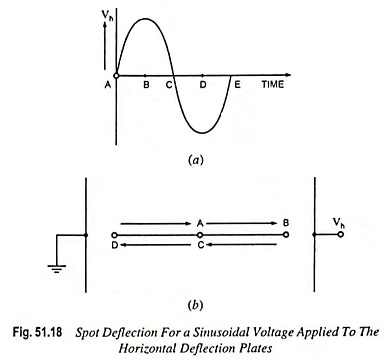
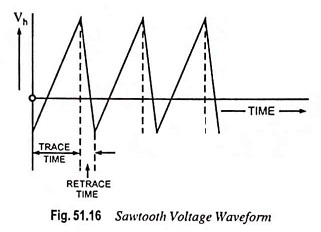
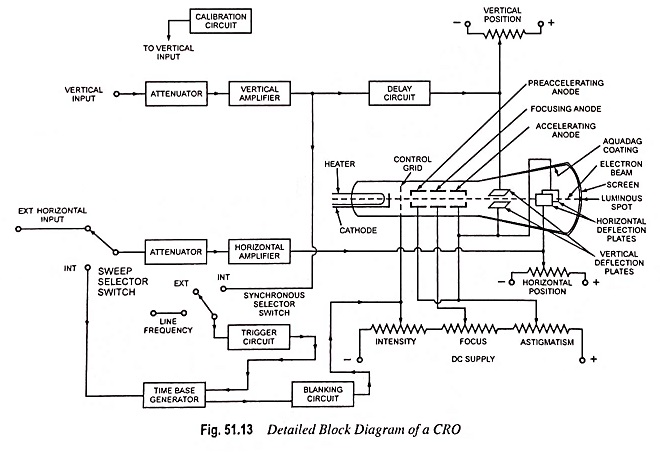
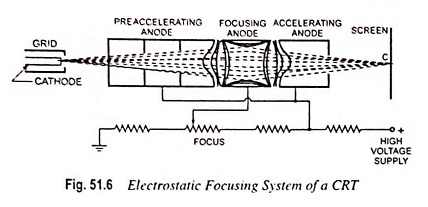
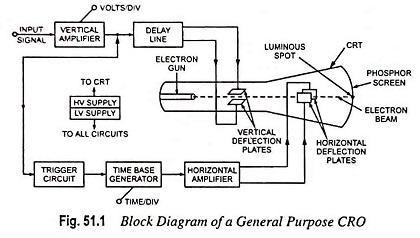
Analog Storage Oscilloscope Block Diagram and Its Workings
Analog Storage Oscilloscope Block Diagram and Its Workings: Storage targets can be distinguished from standard phosphor targets by their ability to retain a waveform pattern for a long time (10 to 150 hours after the…