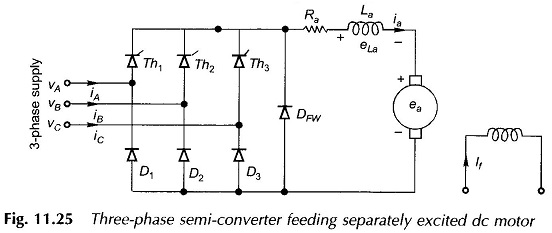
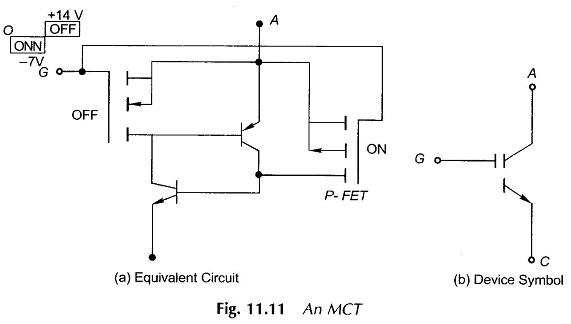
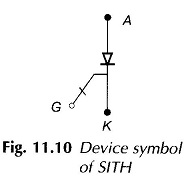
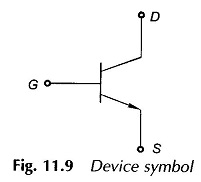
Three Phase Semi Converter feeding Separately Excited DC Motor
Three Phase Semi Converter feeding Separately Excited DC Motor: Large-kW motors are fed from 3-phase supply through three Phase Converters. In a three Phase Semi Converter, the ripple frequency of the motor terminal voltage is…