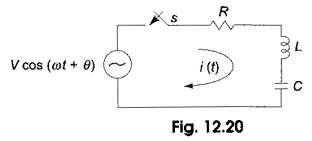
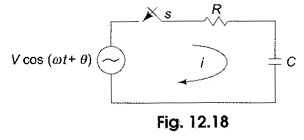
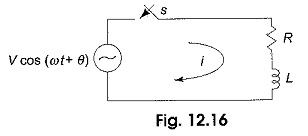
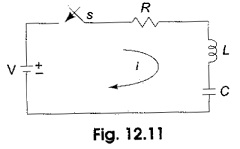
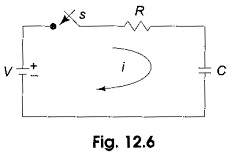
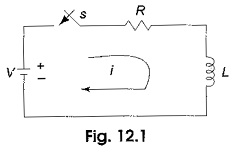
Inverse Transformation
Inverse Transformation: We already discussed Laplace transforms of a functions f(t). If the function in frequency domain F(s) is given, the Inverse Transformation can be determined by taking the partial fraction expansion which will be…