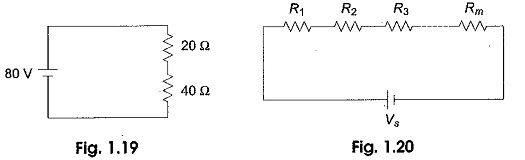
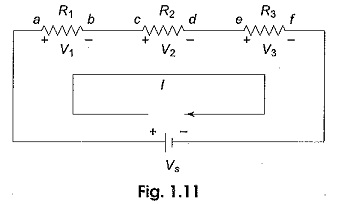
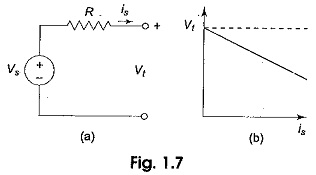
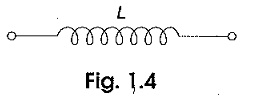
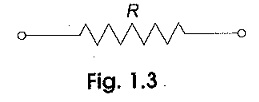
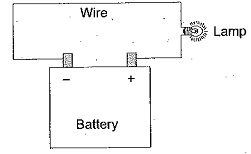
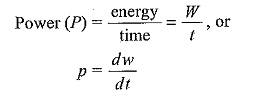Voltage Divider Circuit Diagram
Voltage Divider Circuit Diagram: The series circuit acts as a Voltage Divider Circuit. Since the same current flows through each resistor, the voltage drops are proportional to the values of resistors. Using this principle, different…