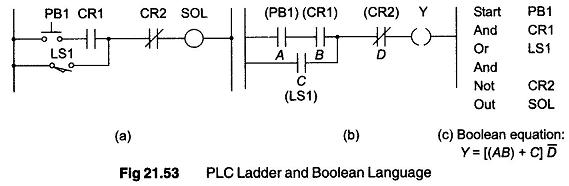
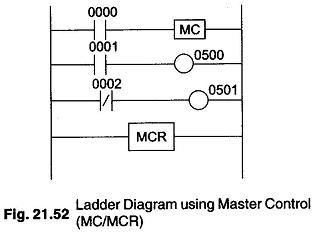
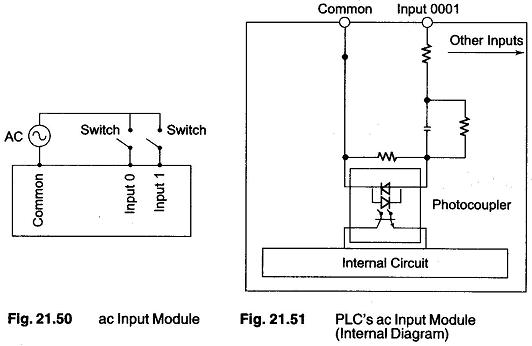
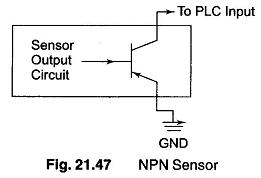
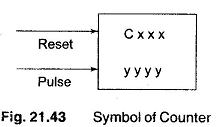
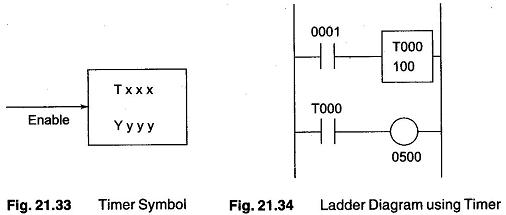
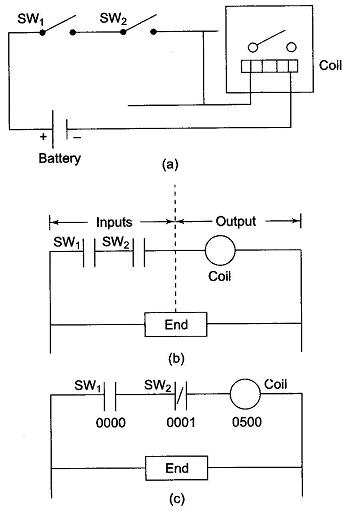
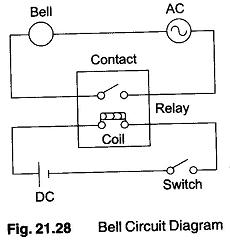
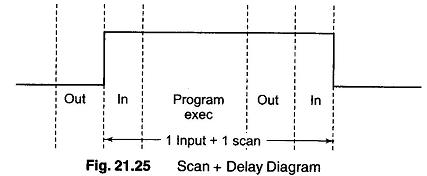
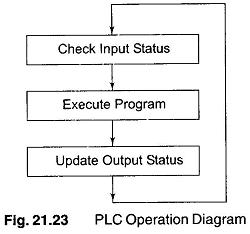
PLC Programming Languages
PLC Programming Languages: The term PLC programming languages refers to the method by which the user communicates information to the PLC. The two most common language structures are ladder diagram language and Boolean language. Ladder…