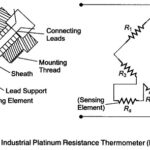
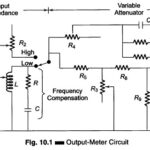
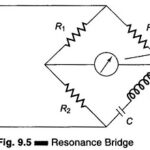
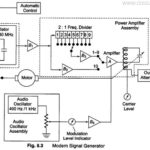
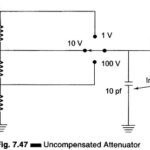
Resistance Thermometer Working Principle
Resistance Thermometer Working Principle: The resistance of a conductor changes when its temperature is changed. This property is utilized for the measurement of temperature. The Resistance Thermometer working principle is…