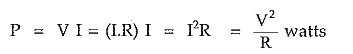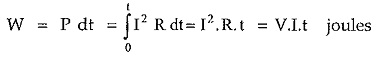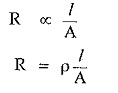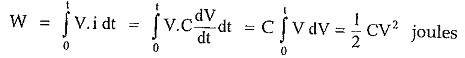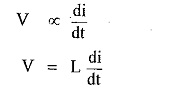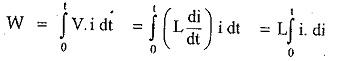Circuit Elements:
Let us take a brief review of three basic Circuit Elements namely resistance, capacitance and inductance.
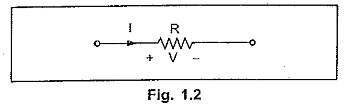
Resistance
It is the property of the material by which it opposes the flow of current through it. The resistance of element is denoted by the symbol ‘R’. Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω).
The relation between voltage and current is given by Ohm’s law.
Resistor dissipates energy in the form of heat. So power absorbed by the resistor is given by,
Resistance converts amount of energy into heat during time t, is given by,
Resistance of a material is directly proportional to its length and inversely proportional to the area of cross-section.
where ρ is constant of proportionality and is known as resistivity or specific resistance, l is length of material and A is cross sectional area of material.
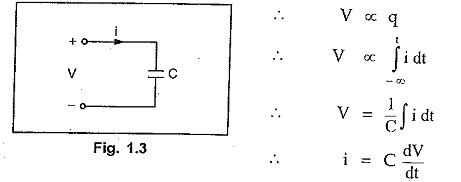
Capacitance
An element in which energy is stored in the form of electrostatic field is known as capacitance. The capacitance is denoted by ‘C’ and it is measured in Farads (F).
For capacitor, the voltage is proportional to the charge.
With zero initial voltage across capacitor, if the current i flows for time t spent, the energy supplied to capacitor will be,
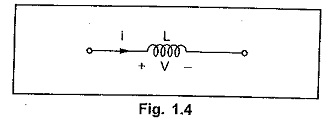
Inductance
Inductance is the element in which energy is stored in the form of electromagnetic field. The inductance is denoted by ‘L’ and it is measured in Henry (H).
For inductance, the voltage is proportional to the rate of change of current.
Assuming that initially zero current flows through the inductance, if a current i is made to flow through a coil, the energy stored in time interval is given by,
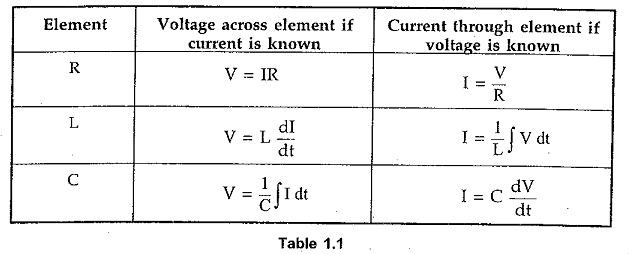
Summarizing the behaviour of the three basic elements, we can write,