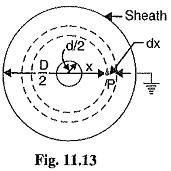
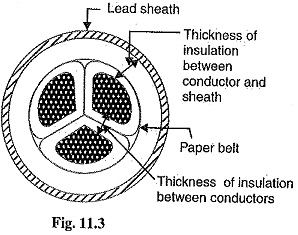
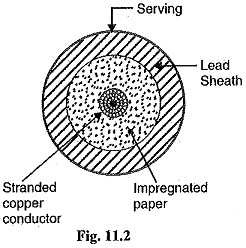
Loop Tests in Underground Cables
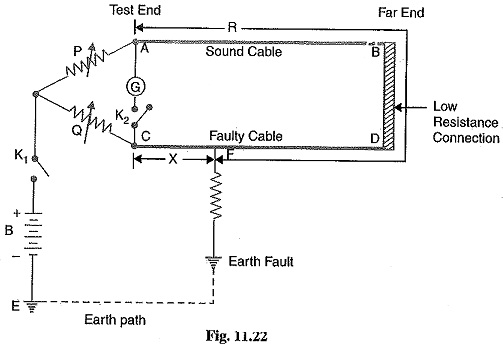
Loop Tests in Underground Cables: There are several methods for locating the faults in underground cables. However, two popular methods known as Loop Tests in Underground Cables are : Murray loop test Varley loop test…