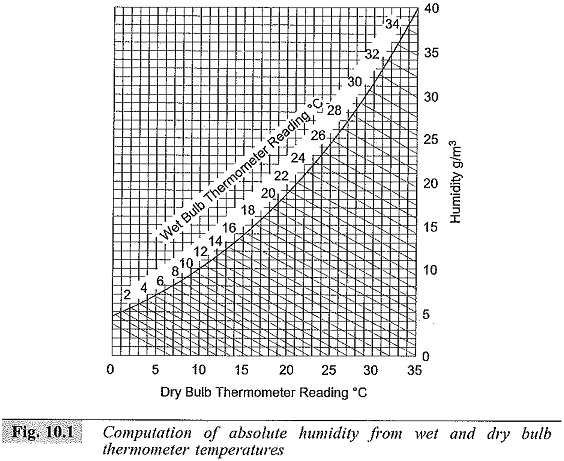
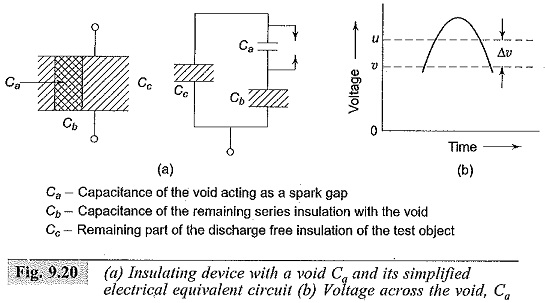
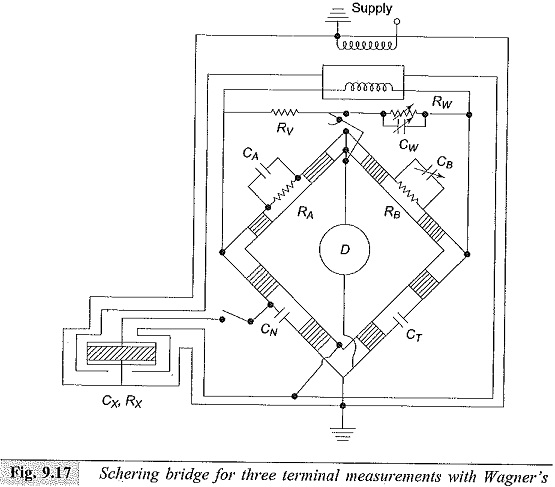
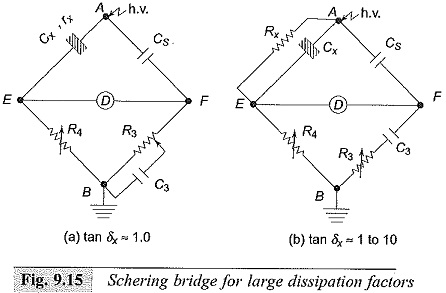
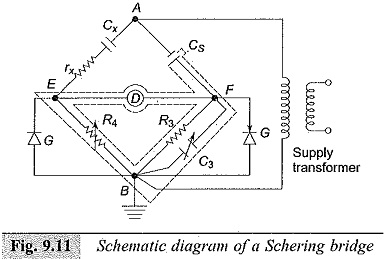
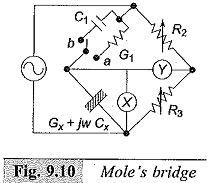
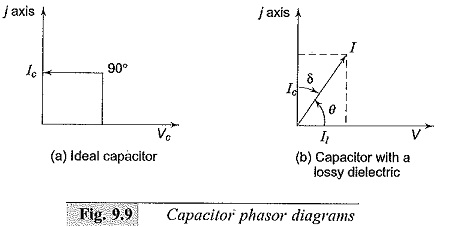
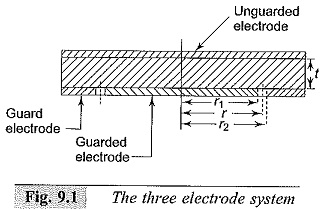
High Voltage Test Bushings
High Voltage Test Bushings: High Voltage Test Bushings Consisting of Three tests, namely Power Frequency Tests Impulse Voltage Tests Thermal Tests Power Frequency Tests: Power Factor—Voltage Test: In this test, the bushing is set up…