Dual Slope Integrating Type DVM
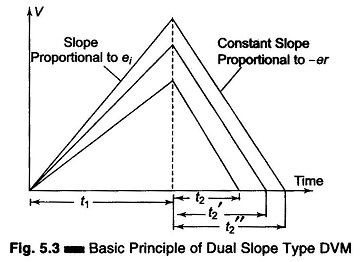
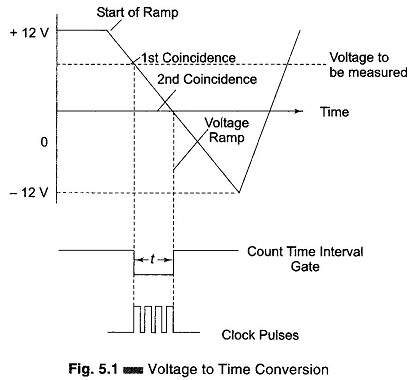
Dual Slope Integrating Type DVM (Voltage to Time Conversion): Dual Slope Integrating Type DVM – In ramp techniques, superimposed noise can cause large errors. In the dual ramp technique, noise is averaged out by the positive and negative ramps using the process of integration. Principle of Dual Slope Type DVM: As illustrated in Fig. 5.3, […]
Dual Slope Integrating Type DVM Read More »