Synchronous Motor and Brushless DC Motor Drives Articles:
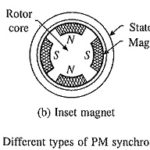
Synchronous Motors Types: Commonly used Synchronous Motors Types are: wound field, permanent magnet, synchronous reluctance and hysteresis motors. All these motors have a stator with a 3-phase winding, which is connected to an ac source. Fractional horse power synchronous reluctance and … (Read More)
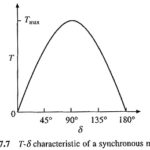
Operation of Synchronous Motor: For any speed other than synchronous speed, the relative speed between air gap flux wave and the rotor is not zero. Consequently, δ varies from 0 to 360°, and torque fluctuates between … (Read More)
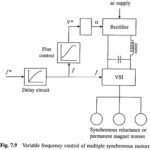
Variable Frequency Control of Multiple Synchronous Motors: A drive operating in true Variable Frequency Control of Multiple Synchronous Motors is shown in Fig. 7.9. Frequency command f* is applied to a voltage source inverter through a delay circuit so that rotor … (Read More)
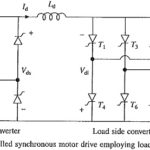
Self Controlled Synchronous Motor Drive: A Self Controlled Synchronous Motor Drive employing a load commutated thyristor inverter is shown in Fig. 7.10. In large power drives wound field synchronous motor is used. Medium power drives also employ permanent magnet synchronous motor. … (Read More)
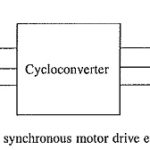
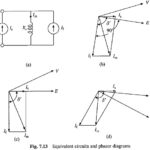
Self Controlled Synchronous Motor Drive Employing a Cycloconverter: Self Controlled Synchronous Motor Drive Employing a Cycloconverter as shown in Fig. 7.13. Firing pulses are generated either by comparison of the motor terminal voltages or by rotor position senors as in the … (Read More)
Sinusoidal PMAC Motor: Since the voltages induced in the stator phases of a sinusoidal PMAC motor are sinusoidal, ideally, the three stator phases must be supplied with variable frequency sinusoidal voltages or currents with a phase difference of 120° between them. … (Read More)
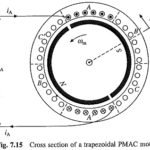
Brushless DC Motor Drives(Trapezoidal PMAC): The cross section of a 3-phase 2 pole Brushless DC Motor Drives is shown in Fig. 7.15. It has permanent magnet rotor with wide pole arc. The stator has three concentrated phase windings, which are displaced … (Read More)