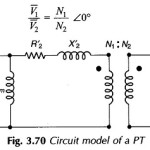
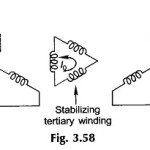
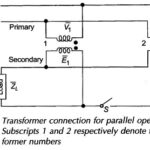
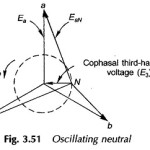
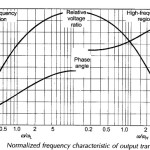
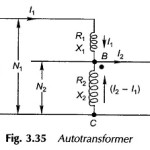
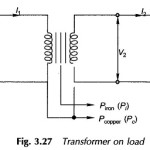
Current transformer and Potential transformer
Current transformer and Potential transformer: These Current transformer and Potential transformer are designed to meet the specific need of measurement and instrumentation systems, which accept voltages in the range of…