Transmission Lines Articles:
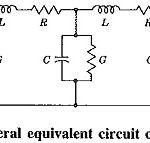
Fundamentals of Transmission Lines: Fundamentals of Transmission Lines (in the context of this book) are considered to be impedance-matching circuits designed to deliver power (RF) from the transmitter to the antenna, and maximum signal from the antenna to the receiver. From such … (Read More)
Losses in Transmission Lines: Types of Losses in Transmission Lines are three ways in which energy, applied to a transmission line, may become dissipated before reaching the load: radiation, conductor heating and dielectric heating. Radiation losses occur because a transmission line may … (Read More)
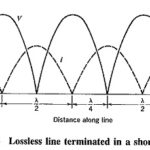
Standing Waves in Transmission Lines: When power is applied to a transmission line by a generator, a voltage and a current appear whose values depend on the characteristic impedance and the applied power. The voltage … (Read More)
 Quarter Wavelength Transmission Line: Sections of transmission lines that are exactly a Quarter Wavelength Transmission Line or Half Wavelength Transmission Line long have important impedance-transforming properties, and are often used for this purpose at radio frequencies. Impedance inversion by Quarter Wavelength lines: Consider … (Read More)
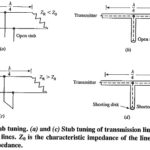
Quarter Wavelength Transmission Line: Sections of transmission lines that are exactly a Quarter Wavelength Transmission Line or Half Wavelength Transmission Line long have important impedance-transforming properties, and are often used for this purpose at radio frequencies. Impedance inversion by Quarter Wavelength lines: Consider … (Read More)Reactance Properties of Transmission Lines: Just as a suitable piece of transmission line may be used as a transformer, so other chosen transmission-line configurations may be used as series or shunt inductive or capacitive reactances. … (Read More)
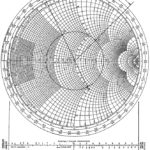
Smith Chart for Transmission Line: The various properties of transmission lines may be represented graphically on any of a large number of charts. The most useful representations are those that give the impedance relations along a lossless line for different load … (Read More)
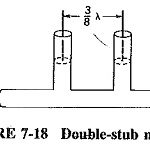
Double Stub Matching: If a transmission-line matching device is to be useful in a range of different matching situations, it must have as many variable parameters, or degrees of freedom, as the standing-wave pattern. Since the pattern has two degrees of … (Read More)
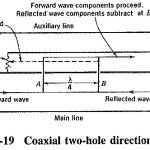
Two Hole Directional Coupler: It is often necessary to measure the power being delivered to load or an antenna through a transmission line. This is often done by a sampling technique, in which a known fraction of the power is measured, … (Read More)
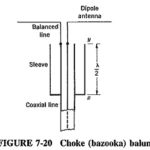
Choke Balun: A Choke Balun, or balance-to-unbalance transformer, is a circuit element used to connect a balanced line to an unbalanced line or antenna. Or, as is perhaps a little more common, it is used to connect an unbalanced (coaxial) line … (Read More)