Data Transmission in Electronic Instrumentation Articles:
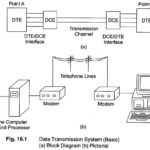
Data Transmission: A data transmission system can be described simply in terms of three components, the transmitter (also called the source), the transmission path (usually referred to as the channel, but sometimes as the line), and the receiver (usually called the … (Read More)
Data Transmission System: A typical data transmission system contains the information source from which data has to be transmitted through a suitable medium to the destination, termed the information sink. The information source can be a computer terminal, a digitized transducer … (Read More)
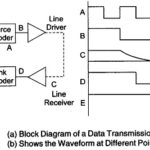
Digital Communication System: Digital Communication System has several distinct advantages over analog transmission systems, but there are definite disadvantages to it as well. Because of the heavy investment in analog facilities, it will be many years before digital becomes the major … (Read More)
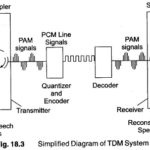
Time Division Multiplexing(TDM): Any pulse modulation scheme involves translating the audio, or modulating signal into a series of encoded pulses, sending these pulses over a transmission medium and reverting the pulses back to an analog signal. Regardless … (Read More)
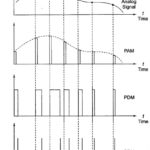
Pulse Modulation: Pulse modulation may be used to transmit analog information, such as continuous speech or data. It is a system in which continuous waveforms are sampled at regular intervals. Information regarding the signal is transmitted only at the sampling times, together … (Read More)
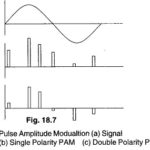
Pulse Amplitude Modulation(PAM): Pulse Amplitude Modulation(PAM) is the simplest form of Pulse Modulation. It is shown in Fig. 18.7. PAM is a pulse modulation system in which the signal is sampled at regular intervals, with each sample proportional to the amplitude of … (Read More)
Pulse Time Modulation(PTM): In Pulse Time Modulation the signal is sampled in the same way as in PAM, but the pulses indicating instantaneous sample amplitudes have a constant amplitude themselves. However, one of their timing characteristics is varied, being directly proportional … (Read More)
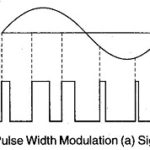
Pulse Width Modulation(PWM): Pulse width modulation of PTM is also often called Pulse Duration Modulation (PDM). In this system, shown in Fig. 18.8, we have a fixed amplitude and starting time of each pulse, but the width of each pulse is … (Read More)
Pulse Position Modulation(PPM): In this Pulse Position Modulation system, the amplitude and width of pulses is kept constant, while the position of each pulse, in relation to the position of a recurrent reference pulse, is varied by each instantaneous sampled value … (Read More)
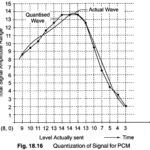
Pulse Code Modulation(PCM): Pulse Code Modulation(PCM) is different from the other forms of pulse modulation studied so far, PCM also uses sampling techniques, but it differs from the others in that it is a digital process. Instead of sending a pulse … (Read More)
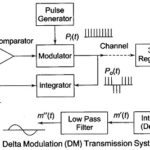
Delta Modulation(DM): Delta modulation(DM) is process of modulation in which train of fixed width pulses is transmitted. Their polarity indicates whether the demodulator output should rise or fall at each pulse. The input is caused to rise or fall by a … (Read More)
Pulse Wave Code Format: There are many different code formats of pulse wave. The classification is based on three criteria, namely, form of information transmission, relation to zero level, and direction. Based on the form of information transmission, the format used can … (Read More)
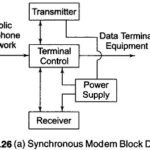
Modem Definition: The term Modem Definition is an acronym for modulator-demodulator. The primary modem function is to convert digital data into an analog form which is suitable for transmission on common carrier circuits (example telephone lines). Modulation is the D/A conversion … (Read More)