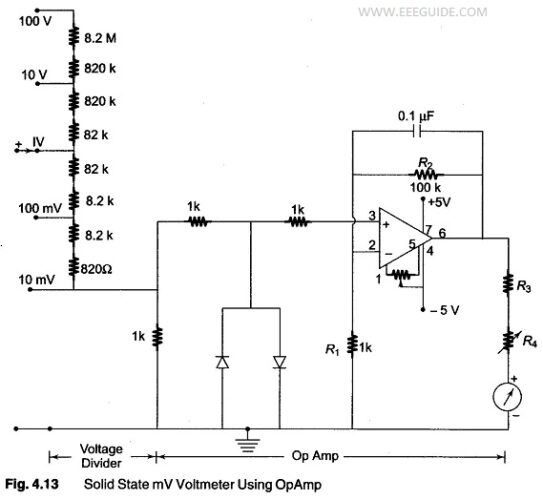
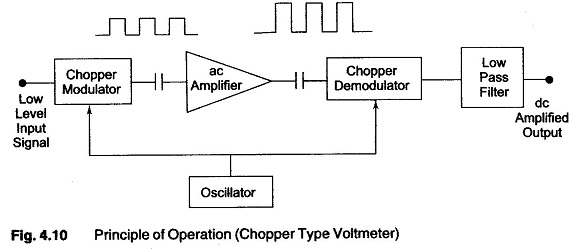
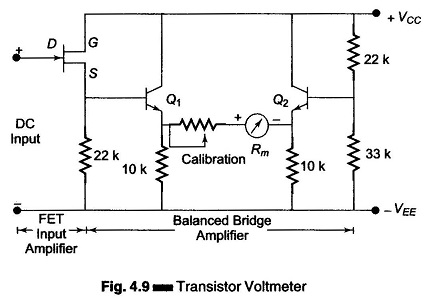
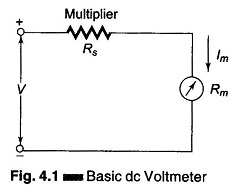
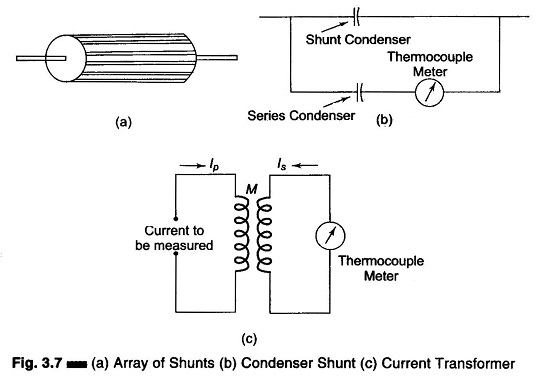
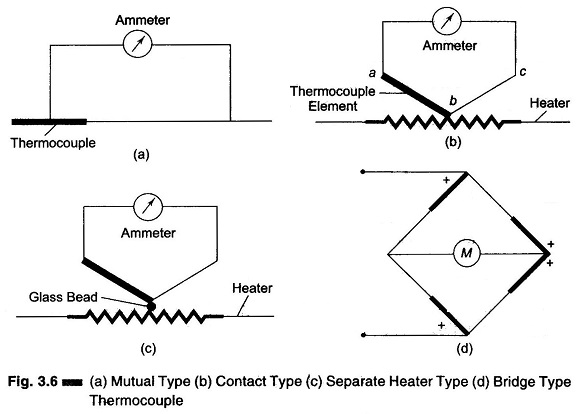
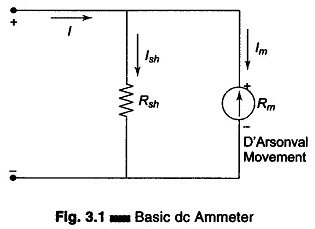
Differential Voltmeter
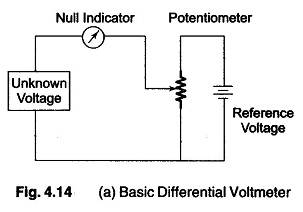
Differential Voltmeter: The Differential Voltmeter technique, is one of the most common and accurate methods of measuring unknown voltages. In this technique, the voltmeter is used to indicate the difference between known and unknown voltages, i.e., an unknown voltage is compared to a known voltage. Figure 4.14 (a) shows a basic circuit of a differential […]
Differential Voltmeter Read More »