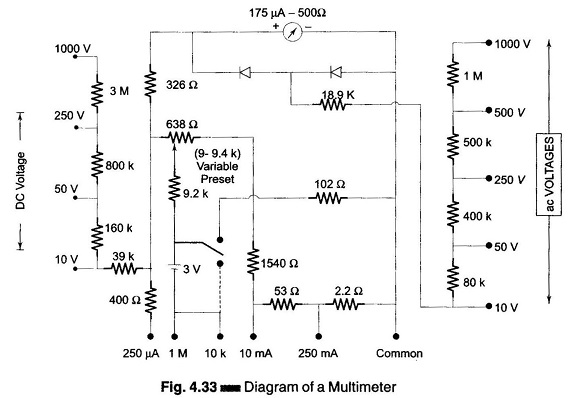
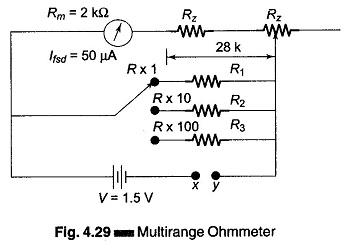
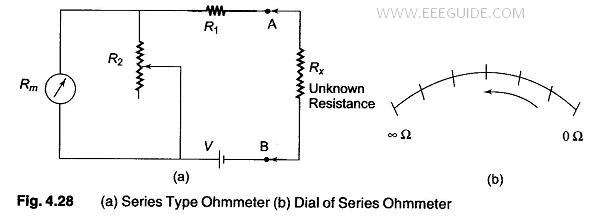
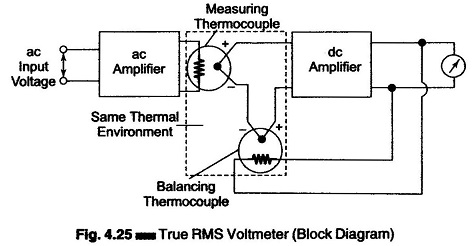
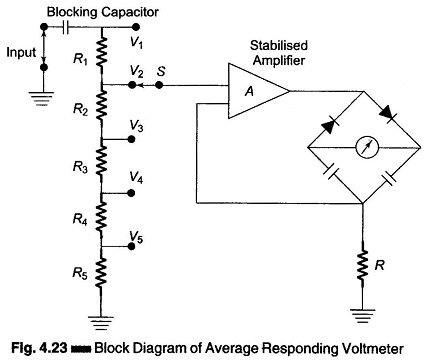
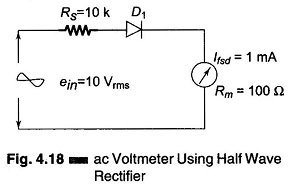
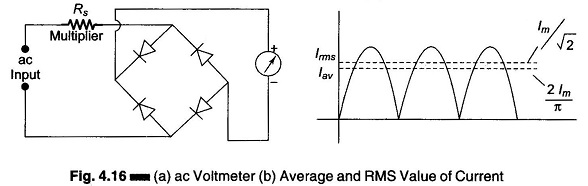
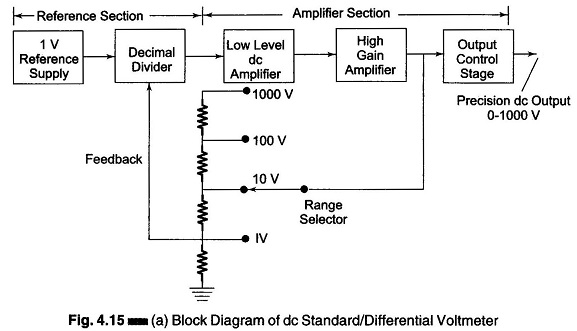
Digital Voltmeters Features and Characteristics
Digital Voltmeters Features and Characteristics: Digital Voltmeters Features and Characteristics which includes measuring instruments that convert analog voltage signals into a digital or numeric readout. This digital readout can be displayed on the front panel and also used as an electrical digital output signal. Any DVM is capable of measuring analog dc voltages. However, with appropriate […]
Digital Voltmeters Features and Characteristics Read More »