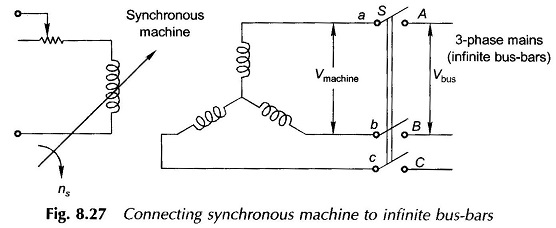
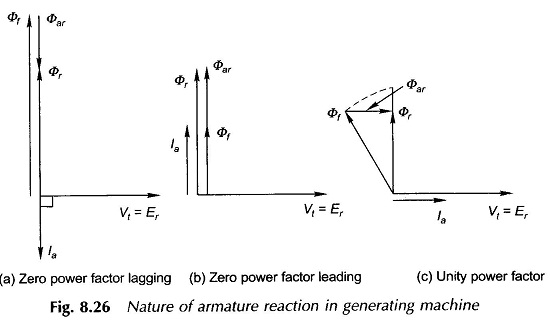
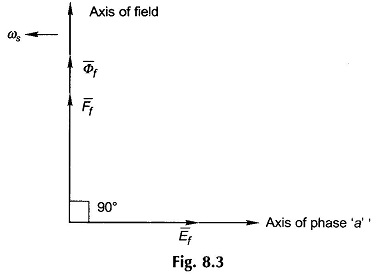
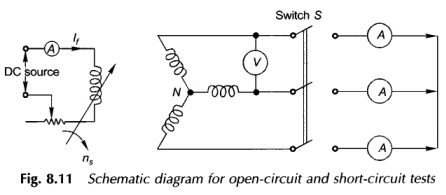
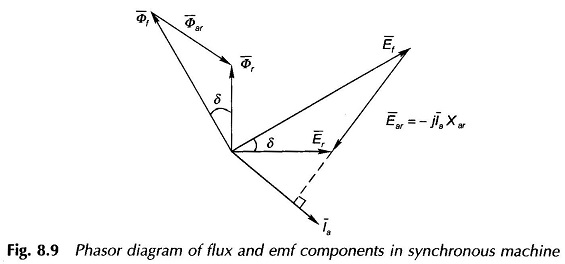
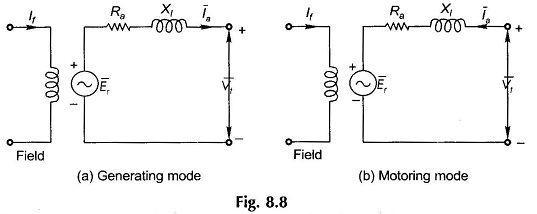
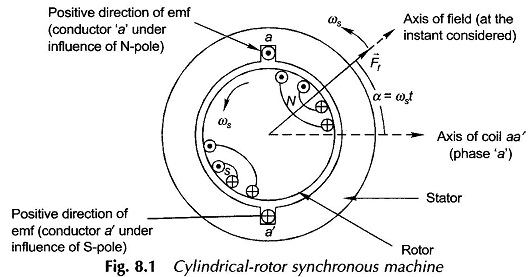
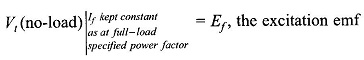Synchronous Machine on Infinite Bus Bars
Synchronous Machine on Infinite Bus Bars: A definite procedure has to be followed in connecting a Synchronous Machine on Infinite Bus Bars which for the present purpose will be assumed to be infinite. Infinite bus-bars…