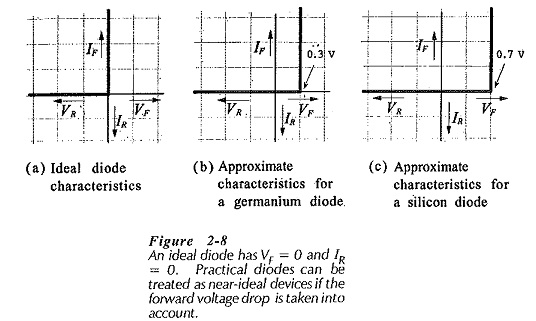
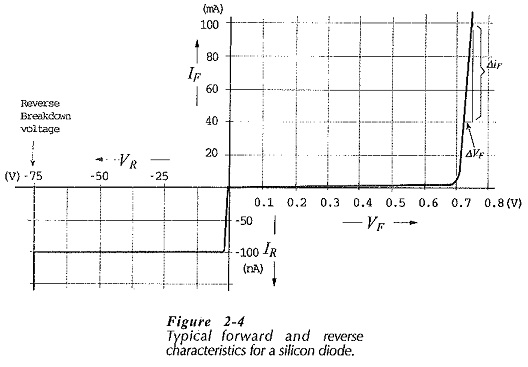
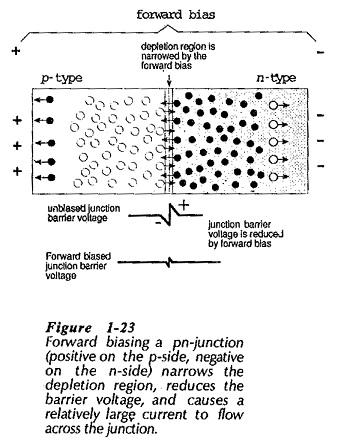
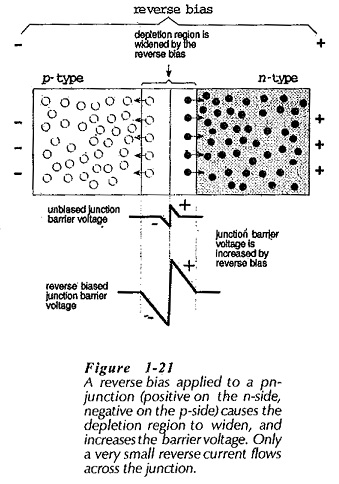
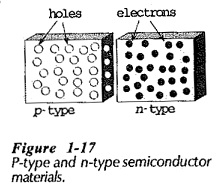
Semiconductor Diode Specifications
Semiconductor Diode Specifications: Diode Data Sheets - To select a suitable diode for a particular application, the data sheets, or Semiconductor Diode Specifications, provided by device manufacturers must be consulted. Portions of typical diode data…