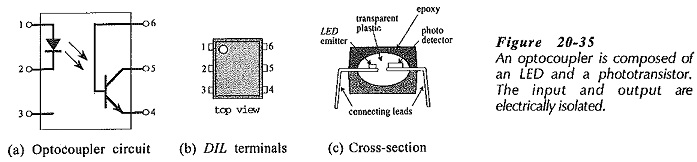
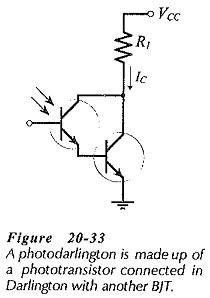
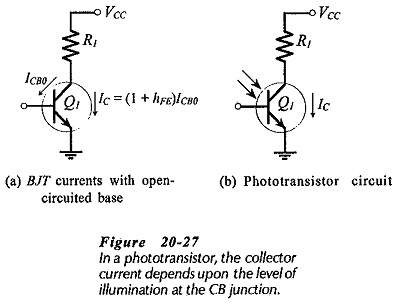
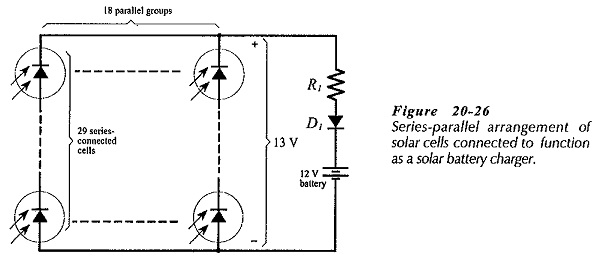
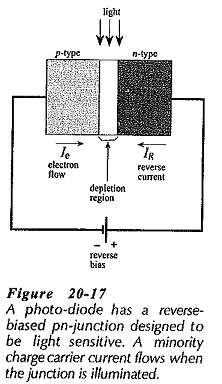
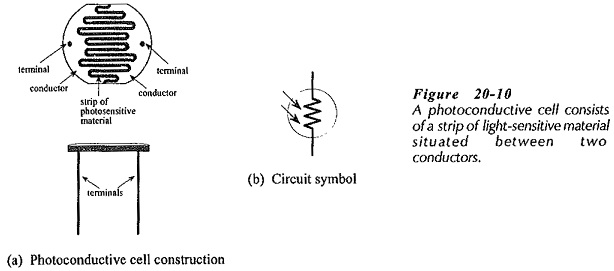
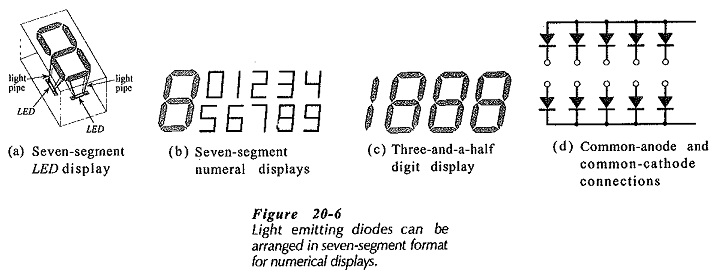
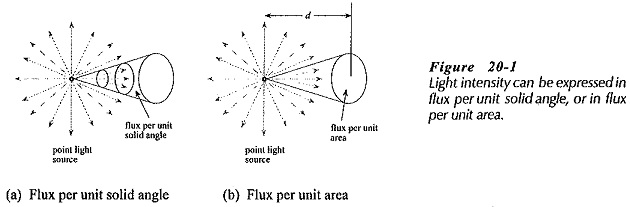
Optocoupler Circuit Operation
Optocoupler Circuit Operation: An Optocoupler Circuit Operation (optoelectronic coupler) is essentially a photo-transistor and an LED combined in one package. Figure 20-35(a) and (b) shows the typical circuit and terminal arrangement for one such device…