Fractional Kilowatt Motors Articles:
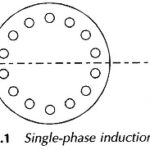
Single Phase Induction Motor: A Single Phase Induction Motor comprises a single-phase distributed winding on the stator and normal squirrel-cage rotor as shown schematically in Fig. 10.1 wherein for convenience the stator winding is shown in concentrated form. There are two important … (Read More)
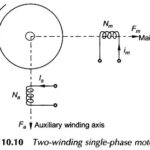
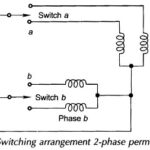
Single Phase Two Winding Motor: To understand the field phenomenon that contributes towards the generation of starting torque in a single-phase motor, it greatly helps to first study a balanced 2-phase motor. Figure 10.10 shows … (Read More)
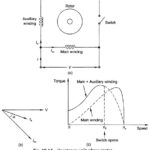
Split Phase Motor: When a motor is provided with two windings, even though these are excited from the same voltage (supply being single-phase), the currents in the two windings can be made out-of-phase by adjustment of the impedance of the auxiliary … (Read More)
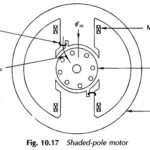
Shaded Pole Motor Working Principle: Figure 10.17 shows a typical Shaded Pole Motor with a squirrel-cage rotor. A small portion of each pole is covered with a short-circuited, single-turn copper coil called the shading coil. The sinusoidally-varying flux created by ac … (Read More)
Difference Between Single Phase and Three Phase Induction Motor: In a 3-phase induction motor the maximum torque is independent of the rotor resistance, while the slip at which it occurs increases … (Read More)
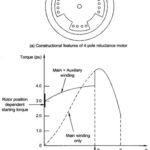
Types of Single Phase Synchronous Motor: There are two types of single phase synchronous motor, namely, Reluctance Motor Hysteresis Motor Construction of Reluctance Motor and Torque Speed Characteristics: The reluctance motor, in general, results wherever the stator produces a rotating field in space and the … (Read More)
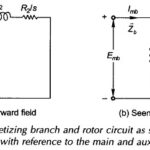
Equivalent Circuit of Single Phase Induction Motor: The winding unbalance and the fact that both the main and auxiliary windings are fed by the same supply result in unbalanced main and auxiliary fields. … (Read More)
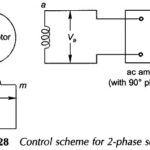
Two phase AC Servo Motor: For a low-power (a few hundred watts) control application, a balanced Two phase AC Servo Motor is ideally suited as it can be driven by means of a relatively rugged (drift-free) ac amplifier. The motor torque … (Read More)
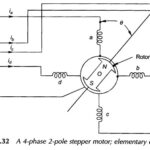
Four Phase Stepper Motor: The stepper motor is a special type of synchronous motor which is designed to rotate through a specific angle (called a step) for each electrical pulse received by its control unit. Typical … (Read More)
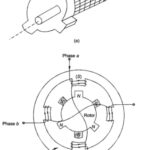
2 Phase 4 Pole Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor: Figure 10.39 shows the phases (stacks) of a 2 Phase 4 Pole Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor. The rotor is made of ferrite or rare-earth material which is permanently magnetized. The stator stack of … (Read More)
Hybrid Stepper Motor Construction and Working: This is in fact a PM stepper motor with constructional features of toothed and stacked rotor adopted from the variable-reluctance motor. The stator has only one set of winding-excited poles which interact with the two … (Read More)
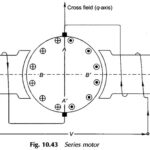
AC Series Motor: A series motor can be run from either dc or ac (single-phase) supply provided that both stator and rotor cores are laminated to limit the iron-loss. Figure 10.43 is the cross-sectional view of a AC Series Motor connected … (Read More)
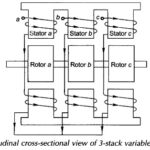
Variable Reluctance Stepper Motor Working Principle: A Variable Reluctance Stepper Motor Working Principle consists of a single or several stacks of stators and rotors-stators have a common frame and rotors have a common shaft as shown in the longitudinal cross-sectional view … (Read More)