Commutation in DC Machine
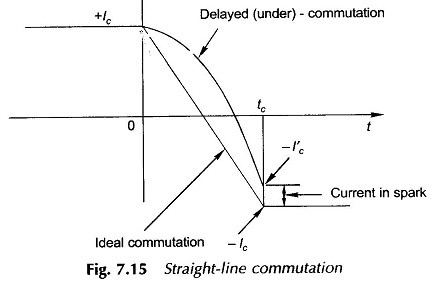
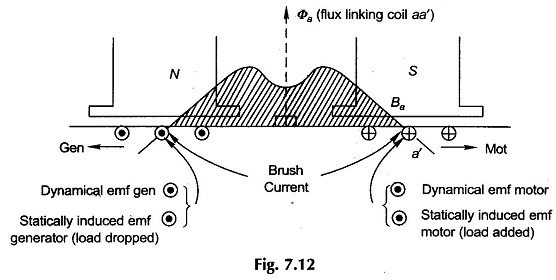
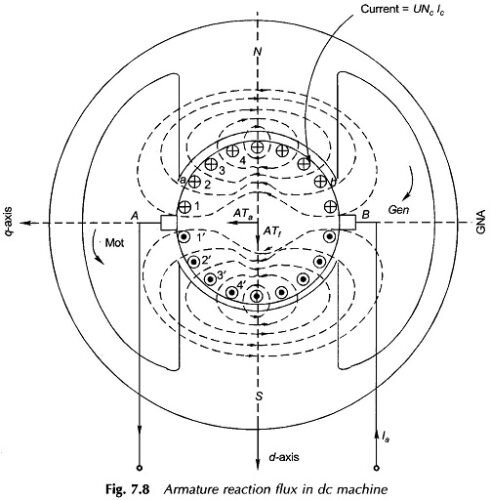
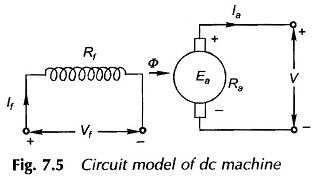
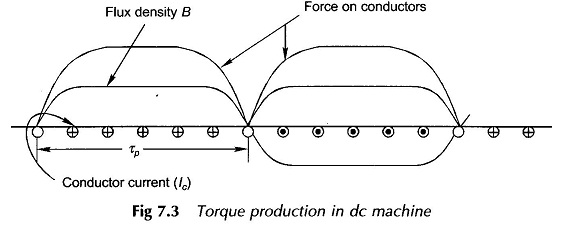
Commutation in DC Machine or Generator or Motor: One coil each under an adjoining pole-pair is connected between adjacent commutator segments in a lap-wound dc armature, while in a wave-wound armature the only difference is that P/2 coils under the influence of P/2 pole-pairs are connected between adjacent segments. Coil(s) current is constant and unidirectional […]
Commutation in DC Machine Read More »