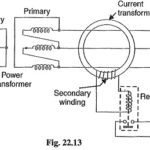
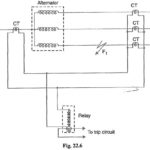
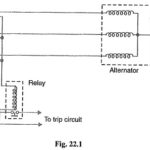
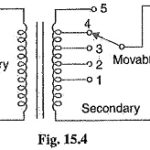
Earth Fault Protection or Leakage Protection
Earth Fault Protection or Leakage Protection: An Earth Fault Protection usually involves a partial breakdown of winding insulation to earth. The resulting leakage current is considerably less than the short-circuit…