Fuses Articles:
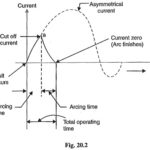
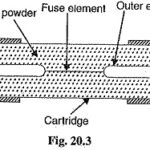
Fuses Definition: Fuses Definition States that : A fuses is a short piece of metal, inserted in the circuit, which melts when excessive current flows through it and thus breaks the circuit. The fuse element is generally made of materials having low … (Read More)
Types of Fuses: Fuse is the simplest current interrupting device for protection against excessive currents. Since the invention of first fuse by Edison, several improvements have been made and now-a-days, a variety of Types of Fuses are available. Some fuses also … (Read More)