Intel 8086 Microprocessor Articles:
Features of 8086 Microprocessor: The features of 8086 Microprocessor are : 1.The 8086 is a 16-bit microprocessor. The term “16-bit” means that its arithmetic logic unit, internal registers and most of its instructions are designed to work with 16-bit binary words. 2.The 8086 … (Read More)
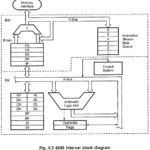
Internal Architecture of 8086: Fig. 6.2 shows a block diagram of Internal Architecture of 8086. It is internally divided into two separate functional units. These are the Bus Interface Unit (BIU) and the Execution Unit (EU). These two functional units can … (Read More)
8086 Addressing Modes: We have seen how the 8086 fetches code bytes from memory by generating 20-bit physical address with the help of IP and CS. We have also seen how the 8086 accesses the stack using SS and SP. In … (Read More)
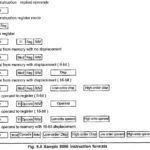
8086 Instruction Format: The 8086 Instruction 8086 Instruction Format vary from 1 to 6 bytes in length. Fig. 6.8 shows the instruction formats for 1 to 6 bytes instructions. As shown in the Fig. 6.8, displacements and operands may be either … (Read More)