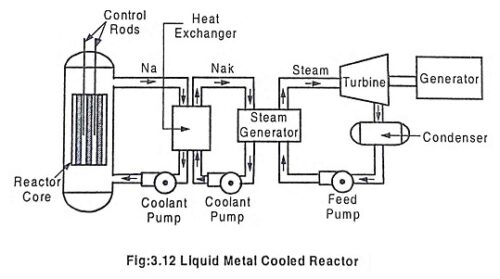
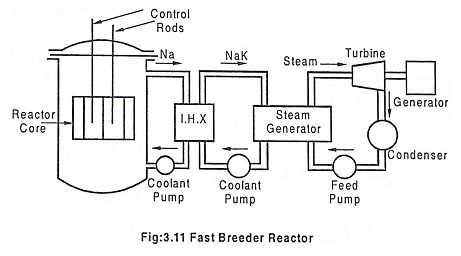
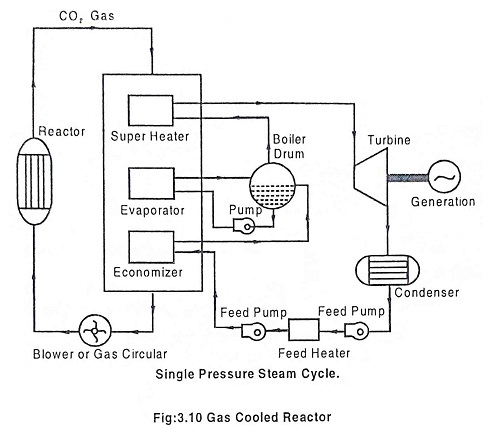
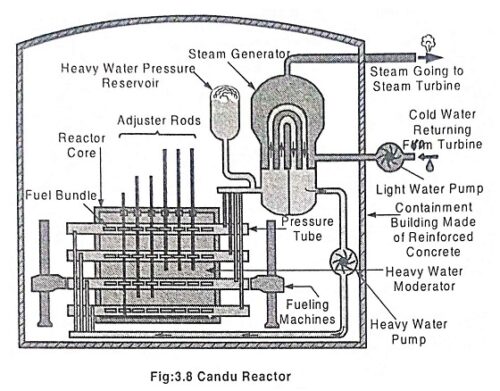
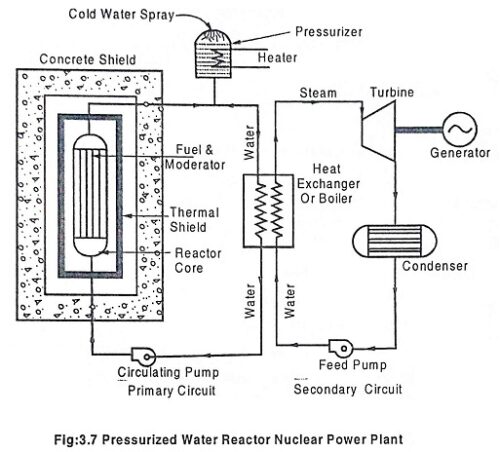
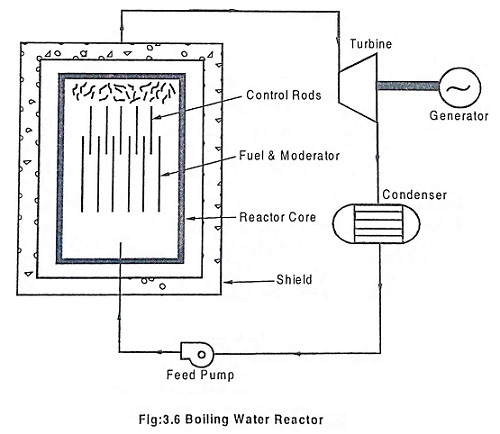
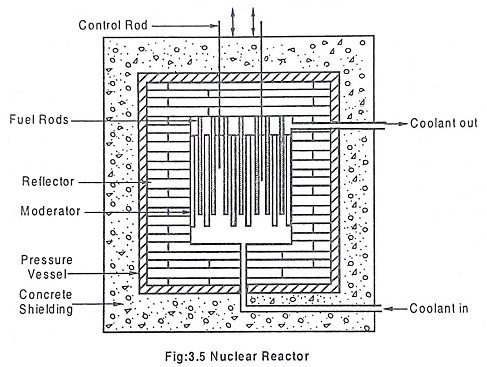
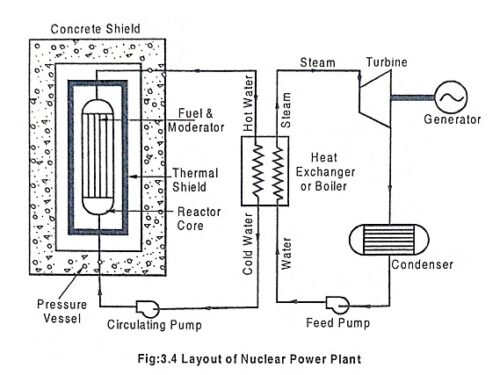
Liquid Metal Cooled Reactor – Working, Advantages & Disadvantages
Liquid Metal Cooled Reactor (LMCR) - Working, Advantages & Disadvantages: A liquid metal cooled reactor (LMCR) is an advanced type of nuclear reactor that uses a liquid metal as the primary coolant. The use of…